wallser Alpen – wikipedia

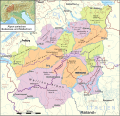
The Walliser Alpen (also Penninian Alps ) are a mountain group in the Western Alps. Switzerland with the canton of Valais and Italy with the regions of Piedmont and Aostatal are part of Switzerland. The mountain group extends over the large area between the Rhone Valley in the north and the Aostatal in the south or between the Simplon Pass in the east and the large Sankt Bernhard in the west. In the driving literature of the SAC from practical considerations, even more extensive from the Griespass on the Nufenenpass in the east to the Eau Noire and Trento in the west.
The highest mountain in the Valais Alps is with 4634 m ü. M. The Dufourspitze in the Monte Rosa massif.
The Valais Alps are record holders among the Alpine groups: they are the Alpine group with the greatest glaciation, and most of the four -thousanders of all Alpine groups are there. They also show the largest height difference within a mountain group in the Alps: between the highest (Dufourspitze, 4634 m ü. M. ) and the deepest point (River Dora Baltea near Ivrea in Piedmont, 253 m) is a height difference of almost almost 4400 m ü. M. The Italian Monte-Rosa-East wall is the highest row of walls in the Alps with a height difference of Fast 3000 m ü. M. ; In the Monte Rosa massif there are numerous of the four thousands.
The Dufourspitze is the highest peak in Switzerland 4634 m ü. M. , during the cathedral with 4545 m ü. M. The highest mountain is completely within Switzerland. The summit pyramids from Matterhorn and Weisshorn are also striking. The highest park in Europe can also be found in the Valais Alps with the Italian nature park Alta Valsesia in the top Val Sesia on the south side of the main ridge. It extends to a height of up to 4559 m ü. M. The highest managed hut of the Alps is Capanna Regina Margherita in 4554 m ü. M. Height on the summit of the signal dice in the Monte-Rosa-Stock.
The traffic in the Valais Alps is led by the Simplon tunnel, among other things, which is the third longest railway tunnel in Switzerland or Italy and the third longest railway tunnels continental Europe (according to the Gotthard and Lötschberg base tunnel). Under the mountain railways, the shuttle railway stings on the Klein Matterhorn, which with a mountain station in 3820 m ü. M. Height is the highest cable car in Europe, and the Metro Alpin at Saas Fee, the highest cable car in the world with a mountain station 3450 m ü. M. , out. The LAC des Dix is the largest reservoir in Switzerland with 400 million m³ of capacity and has the highest weight dam in the world at 284 m.
Four -thousand meter [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
There are 41 four -thousanders in the Valais Alps, 36 of which are piling up around the Matter Valley, which is the largest concentration of main peaks of the four -thousanders in the Alps. [first] This also includes half of all four thousands of the Alps in the Valais Alps. The other half of the four -thousanders are spread over five other mountain groups in the Alps.

More summit [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
- This sub -group of the Valais Alps [2] is described separately under Leone group.
Landscapes of national importance (Switzerland) [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
According to Article 5 of the Federal Law on Nature and Homeland Security, Switzerland leads a federal inventory of landscapes and natural monuments of national importance.
There are currently seven of these landscapes in the Valais Alps:
- No. 1701, name: Binnal , Year of the admission to the inventory: 1977, size: 5084 ha, not impaired Alpental with small lakes by interventions; Geologically very versatile; unique find area for minerals; Exceptionally rich flora
- No. 1703, name: Val de Bagnes , Year of admission to the inventory: 1977, size: 16,869 ha, heavily glaciated high mountain landscape; diverse flora and fauna; Significant stone wild colony
- No. 1707, name: Dent Blanche-Matterhorn-Monte Rosa , Year of admission to the inventory: 1983, revision: 1996, size: 26,942 ha
- No. 1708, name: Euseigne pyramids , Year of admission to the inventory: 1983, size: 70 ha
- No. 1716, name: Pfynwald-Illgraben , Year of admission to the inventory: 1998, size: 5074 ha
- No. 1717, name: Laggintal-Zwischenbergtal , Year of admission to the inventory: 1998, size: 11,498 ha
- No. 1718, name: Val the rude-sassesire , Year of admission to the inventory: 1998, size: 3480 ha
Long-distance/long hiking trails [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
The Via Alpina, a cross -border long hiking trail with five partial paths through the entire Alps, also runs through the Valais Alps. The Blue path of Via Alpina runs with 20 stages through the southeastern, Italian part of the Valais Alps with a short detour to the Swiss side.
Hut [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
Passport [ Edit | Edit the source text ]
Due to the large differences in altitude and the glossy, there is no pass crossings that can be accessed for motorized traffic in the Valais Alps between the Great Sankt Bernhard and the Simplon. There are some passports that are accessible via the moor path, hiking trails or with skis. The Theodul Pass between Matterhorn and Breithorn and the Adler Pass in the Mischabel-Group are known. The Saastal is connected to the Italian Val d’Ossola through the Zwischerbergenpass via Gondo and through the Monte Moro Pass via the Valle Anzasca.
- ↑ Mattertal. Federal Office for Landestopography Swisstopo, accessed on April 13, 2016 .
- ↑ Ernst Höhne: Knaur’s lexicon for mountain fans / the Alps between Matterhorn and Lake Constance . Droemer Knaur, Munich 1987, ISBN 3-426-26223-1, S. 124 f .

Recent Comments