Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet – Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, Liberade Libera.
| Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet | |
|---|---|
 An F/A-18F Super Hornet of the US Navy leads a mission above the Persian Gulf |
|
| Description | |
| Type | Multural hunting boarded |
| Crew | 1 in the single -seater version, therefore e
2 In the two -seater versions, therefore F and G |
| Designer | |
| Manufacturer | |
| First flight date | November 29, 1995 |
| Date entry into service | 1999 |
| Main user | |
| Other users | |
| Specimens | 608 (2020) [first] |
| Unit cost | US $ 51 Milion (2019) [2] |
| Developed by | McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet |
| Other variants | Boeing E/A-18G Growler |
| Dimensions and weights | |
 Perspective tables |
|
| Length | 18,31 m |
| Wingspan | 13,62 m |
| Height | 4,88 m |
| Wing surface | 46,5 m² |
| Empty weight | 14 552 kg |
| Max weight on take -off | 29 937 kg |
| Fuel capacity | 6 780 kg (in the single -seater version), 6 354 kg (in the two -seater versions) |
| Propulsion | |
| Motor | 2 turbofan General Electric F414-GE-400 con postbruciatore |
| Push | from 62.3 kn (without postbrier) to 97.9 kn (with postbrier) each |
| Performance | |
| Max speed | ~ 750 nodi (~ 1.400 km/h)
1.2 but at sea level |
| Uphill speed | 228 m/s |
| Autonomy | 2 346 km |
| Action range | 722 km |
| Tangence | ~ 60 000 feet (20 200 m) |
| Weaponry | |
| Cannons | 1 M61 Vulcan da 20 mm |
| Bomb | free fall : Mk 82 and 500 lb MK 83 and 1000 lb MK 84 and 2000 lb cluster : nuclear : |
| Missiles | air air : 2 AIM-7 Sparrow 4 AIM-9 Sidewinder 2 AIM-120 AMRAAM 4 AIM-132 ASRAAM 4 IRIS-T air surface : |
| piling | 6 sub-poles 3 Under the fuselage 2 wing ends |
| Other | Litening Aflir ECM Chaff and Flare via Suu-42a/a AN/alq-99 |
| Note | Data relating to the version: F/A-18E/F |
| Voices of military planes on Wikipedia | |
The Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet , initially known as McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Super Hornet , is a multi-row Bimotore hunting Based on McDonnell Douglas f/a-18 Hornet produced by Boeing. It is an enlarged and advanced version of the F/A-18C and D of the Hornet.
Designed and initially produced by McDonnell Douglas, Super Hornet flew the first time in 1995. Large production began in September 1997, after the merger of McDonnell Douglas and Boeing the previous month. The Super Hornet entered service at the United States Navy in 1999, replacing the Gumman F-14 Tomcat, which was withdrawn in 2006, and serves next to the original Hornet.
The Royal Australian Air Force (Raaf) began to use the F/A-18A as the main hunting aircraft since 1984, and also purchased f/a-8f in 2007 to replace the now obsolete F-111. The Super Hornet entered service at the Raaf in December 2010.
It was ordered and delivered in 565 specimens in the versions and F for United States Navy and in 24 specimens of the F version for the Royal Australian Air Force. Recently it seems that the German Ministry of Defense is interested in the purchase of 40 hunting specimens to replace the Panavia Tornado. [3] It has an internal 20 mm M61A2 cannon, it can load air-air missiles, air-surplus missiles and bombs. It can load additional fuel in five external tanks, it can also be configured as a retainer in flight.
The F/A-18E single-seater and the two-seater f/A-18F, officially nominated Super Hornet and unofficially by the Rhino operators, bear the name and concept of the most updated original versions Hornet (the now withdrawn versions C and D), but redesigned from the Boeing. They have entered production since 1995, and have been on duty since 1999. The changes are many, starting from the surface of the enlarged airframe of 25%, wider and rectangular air intakes, the magnification of the Slats on the foldable part of the wings and new F414 engines, the final variant of the traditional F404. In addition, the Super Hornet also changed in the Avionics, replacing the UFC keyboard with a fourth touch screen multifunction display, replacing the old Ifei (Integrated Fuel/Engine Indicator) panel with another display and changing provisions of some panels and keys, Like the electronic war panel, the RWR panel, the wings folding selector, the update of the external light panel and the replacement of the already present multifunction display. Like the old f/a-8D variant, the most updated f/a-8f has the possibility to bring an instructor in the rear cockpit, an instructor employee.
- F/A-18E : single -seater series version.
- F/A-18F : version of a two -seater series.
- E/A-18G Growler : electronic war version of the f/a-18f Super Hornet. He entered low production in 2007, employed by the US Navy in 2009. The E/A-18G replaces the U.S. Navy the Northrop Groumman EA-6B Prowler.
- Super Hornet Block III : new variant of the huntbombardiere boarder Super Hornet, called Super Hornet Block III, proposed by Boeing to complement the F-35C fleet of the US Navy over 2030. The Block III differs from the Advanced Super Hornet, for the fact that the emphasis is now located no longer on improving the stealth capacity of the aircraft, but on the increase in networking skills. The goal, in fact, is to make the Super Hornet an intelligent node of the US Navy IFC-CA (Naval Integrated Fire Control-Counter Air) become. To do this, Boeing proposes the installation on the “Super” VelvaD Targe Processor-Networked (DTP-N) and high-speed Data-Link, based on IP protocol, Targeting Netchnology (TNT) aircraft. To these changes must then be added a new cockpit with a “Large-area” display 10×19 inch of Elbit, similar to the one proposed for the aircraft with which Boeing runs together with Saab for the T-X race and for any future EF Export variants -15E Strike Eagle. The package of changes also include other updates already planned for the Super Hornet Advanced or which are in acquisition for Super Hornet in service. Among these, the long-haul Irst Lockheed Martin An/Asg-34 (V) 1, compliance tanks of 3500 Gallons, which would increase the range of the 150 Nm aircraft and the “time on station” up to half an hour, The Integrated Defensive Electronic Countermeasures (idecm) An/Alq-214 of Harris and improvements to the Aesa Raytheon APG-79 radar. At the moment, however, the adoption of the new F414-GE-400 engine is not understood. [4]


 Australia
Australia
- 24 f/A-18F Block II ordered in 2007 to replace the F-111. [5]
 Kuwait
Kuwait
- On 29 September 2016 the White House gave the green light to the sale of 28 f/a-18 and/f (22 f/a-18E and 6 f/a-18F, plus an option for a further 12 specimens) for the Kuwait for a value of $ 10.1 billion. [6] [7] [8] [9]
The supply, approved by the American State Department on November 17, 2016, also includes 41 Aesa radar, various armaments, spare parts and logistical support. [ten]
 United States
United States
- 300 in service on May 2018, but the planned acquisitions should bring the specimens to 573 and all of the Block III variant. [11]
-
- Pacific fleet
- Atlantic fleet
- Test and evaluation unit
- VX-9 “Vampires” (Air Test and Evaluation Squadron, operates with F/A-18F and other planes
- VX-23 “Salty Dogs” (Air Test and Evaluation Squadron, opera con F/A-18F e altri aerei
- VX-31 “Dust Devils” (Air Test and Evaluation Squadron, opera con F/A-18F e altri aerei
- NSAWC (Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center), operates with F/A-18F and other planes
Both United States Navy and Royal Australian Air Force have a total of 12 aircraft for squadron.
 Swiss
Swiss
In 2012, Switzerland announced the Saab Jas 39 Grpen as a winner in the armament program which provided for the acquisition of 22 hunting 4+/4 ++ generation for its air force. The Saab Jas 39 Grpen, the Eurofighter Typhoon, the Dassault Rafale and the Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet participated in the assignment (the latter was subsequently withdrawn by Boeing, who realized that he was out of the competition in the competition, due to the too high cost of your specimen).
In 2022 Switzerland has not yet ordered the F-35.
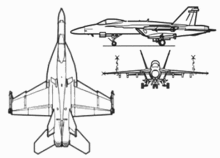



General characteristics
- Crew : F/A-18E 1, F/A-18F 2
- Length : 18,31 m
- Wingspan : 13,62 m
- Height : 4,88 m
- Wing surface : 46,5 m²
- Empty weight : 14 552 kg
- Load weight : 21 320 kg (in hunting configuration)
- Maximum take -off weight : 29 937 kg
- Propulsion : 2 x General Electric F414-GE-400 turbofans
- Internal fuel : F/A-18E: 6 780 kg, F/A-18F: 6 354 kg
- External fuel : 5 × 480 gal tanks, total 7 381 kg
Performance
- Full speed : Mach 1,8 (1 915 km/h) a 13.190 m
- radius : 2 346 km (1 275 nmi) with two AIM-9
- Action : 722 km (390 nmi) Missions forklift
- Transfer : 3 330 km (1.800 NMI)
- Tangence : 15 000 m
- Rate of climb : 228 m/s
- Wing load : 459 kg/m²
- Pushing/weight ratio : 0.93
- Load factor : 7.6g
Armament and Avionics
- ^ Copy archived . are navy.mil . URL consulted on June 30, 2020 (archived by URL Original May 31, 2020) .
- ^ https://nationalinterest.org/Blog/buzz/navy-Getting-newer-and-better-fa-18ef-super-Hornnets -its-criers-1119936363636
- ^ “Can Germany have ordered the first Super Hornet F-18s to start replacement of tornadoes?” , on Aviatio-report.com April 21, 2020 URL consulted on 25 May 2020.
- ^ “Here is the Super Hornet Block III” , on Portaledifesa.it, 12 April 2017, URL consulted on April 12, 2017.
- ^ “The future of Australian defense” – Aeronautica & Defense “N. 364 – 02/2017 PP. 52-55
- ^ “BOEING CONTRACTED TO BUILD SUPER HORNET FIGHTERS FOR KUWAIT” Filed On June 28, 2018 in the Internet Archive., On Janes.com, 27 June 2018, URL consulted on 27 June 2018.
- ^ “US defense: green light for the sale of hunting in Qatar, Bahrain and Kuwait” , on Defenseonline.it, 29 September 2016, URL consulted on 29 September 2016.
- ^ “The Emirates of the Gulfo full of American huntbubeders” , Sualisidifesa.it, 5 October 2016, URL consulted on November 3, 2016.
- ^ “The air forces of the world. Kuwait” – “Aeronautica & Defense” N. 429 – 7/2022 pag. 70
- ^ “KUWAIT, QATAR DEALS MOVE FORWARD, LIKELY PUTTING BOEING FIGHTER JET PRODUCTION INTO THE 2020s” , on DefensNews.com, 17 November 2016.
- ^ “BOEING LAUNCHES SUPER HORNET SLM MODIFICATION” Filed On 7 May 2018 on the Internet Archive., On Janes.com, 4 May 2018, URL consulted on May 7, 2018.
- ( IN ) Greg Goebel, [2.0] Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet . are AirVectors , http://www.airvectors.net , April 1, 2007. URL consulted on 9 March 2009 .
- ( IN ) Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Block II ( PDF ), are Boeing , http://www.boeing.com/ , 2008. URL consulted on 9 March 2009 .
- ( IN ) Boeing / McDonnell Douglas / Northrop F/A-18 Super Hornet . are Military dictionary , http://www.militaryFactory.com , December 24, 2008. URL consulted on 9 March 2009 .
- ( IN ) F/A-18 Hornet . are Federation of American Scientists , http://www.fas.org/index.html , April 25, 2000. URL consulted on 9 March 2009 .
Recent Comments