Sulttanat de lingga-riau — Wikipedia
A wikipedia article, free l’encyclopéi.

The Sultanat de Lingga-Riau is a princely state of Indonesia which existed from 1819 to 1911.
The name of this kingdom has changed over time, depending on the location of its capital. At XVII It is century, he was known as “Johor’s sultanate”, at XVIII It is Siècle, “Riau-Lingga” et à split des mandirons of 1790, “lingga-riau” [ first ] .
Until the beginning of XIX It is century, Lingga, like the rest of the riau, was part of Johor’s sultanate. At XVIII It is A century again, Riau was the main warehouse on the maritime road ranging from India to China.
In 1722, bugis troops recruited by Johor’s sultan pushed a Minangkabau attack. As a reward, the Sultan grants their leader the title of Yamtuan Muda (“viceroy”), which will become hereditary. The Sultan Malays and his court resided in Daik on the island of Lingga. The Yamtuan Muda Bugis and his relatives resided on the island of Penyengat, which was the true heart of the kingdom. The bugis indeed constituted the elite both secular and religious of Riau.
In 1784, the sultanate attacks Malacca without success, then controlled by the Dutch. This failure will weaken Johor.
In 1819, Raffles founded Singapore on an island which he rented to the sultan of Johor.
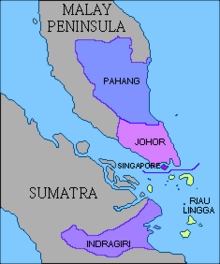
The London Treaty of 1824 between the English and the Dutch Malaysian World Cup in two. Malaysian identity is divided between the east coast of Sumatra and the peninsula. Riau is separated from the rest of Johor’s sultanate and forms Lingga’s rival sultanate [ 2 ] .
The Dutch impose their “protectorate” at the Sultanate of Lingga in 1830. Singapore eclipses soon Riau as a regional trade center.
Bugis princes dominate the religious life of Riau. They have the reputation of promoting reformist ideas. In 1857 – 1858, the Yamtuan Muda Raja Haji Abdullah is murshid (Spiritual Guide) of Tariqa Naqshabandiya, a mystical Sufi brotherhood linked to Turkey. According to the Tuhfat Al-NAFIS (see below), all the Penyengat princes belonged to this audiqa . On the death of Raja Abdullah in 1858, Raja Muhammad Yusuf Luis succeeded.
In 1866 in Penyengat, the religious scholar and moral historian Raja Ali Haji (1809 – 1870) finished the editorial staff of the Tuhfat Al-NAFIS (“The precious gift”), an epic relating the actions of his Bugis ancestors in the Malaysian world started by his father, Raja Ahmad (born in 1773). The book deals with reasons for disputes between Malay and Bugis. He praised the Yamtuan Muda Raja Ja’far (reign 1805 – 1831).
Taking the pretext of marriage bonds that have become very close between the aristocracies Malaise and Bugis, the Dutch decide not to name Yamtuan Muda to death in Raja Muhammad Yusuf, who had fulfilled this function for 40 years. Her son Raja Ali Kelana was reluctant to succeed him. This 1900 “diktat” puts an end to the power of the Bogis in Riau.
- Virginia Matheson, , “Strategies of Survival: the Malay Royal Line of Lingga-Riau”, Journal of Southeast Asian Studies , vol. XVII, no. 1, Mars 1986
- EHITO KIMURA, Political Change and Territoriality in Indonesia: Provincial Proliferation , Routledge, New York (2013), p. 99
- Haller-Rost, Renate, Historical Legal Claims: a Study of Disputed Sovereignty Over Batu Puteh Island/Pedra (1993)
- Kimura, ehito, Political Change and Territoriality in Indonesia: Provincial Proliferation , Routledge, New York (2013)
- Matheson, Virginia, “Strategies of Survival: the Malay Royal Line of Lingga-Riau”, Journal of Southeast Asian Studies , vol. XVII, no. 1,
Recent Comments