Ground Infinite Wireless -Wikipedia
Ground -based radio (Chijokibanmusen, TErrestrial Trunked RAdio 、 TETRA ) Is a business digital mobile communication system for specific applications that are designed for government agencies, special emergency services, police, fire departments, ambulances, rail transport employees, transportation services, and military use. 。 Published in 1995 by the European Telecommunications Standardization Organization and was recognized by the European Electric Communications Standardization Organization (ETSI). In Japan, the Radio Industry Association has standardized as STD-T80.
Previously, it was called Trans-European Trunked Radio. It is a European standard of a wireless trunk system and a professional mobile radio [first] And two -way transceiver specifications. TETRA was specially designed for government agencies, emergency services (police, fire departments, ambulances, ambulances), railway radio rail transport staff, transport services, and military use. [2] TETRA, like Project 25, is a European trunk radio.
TETRA is the first version of the European Electric Communications Organization (ETSI) released in 1995. It is mentioned by the European Radio Committee (ERC). [3]
TETRA is a wireless carrier with four user channels, and uses a division multiple connection at a 25kHz carrier interval. In order to send information, a digital modulation method of π/4 DQPSK is used due to phase biased modulation. The standard also includes low -data rate digital data transmission. Normal communication is secured even when overloaded in large -scale public events and disasters, and can be connected to a calling partner at any time.
Unlike mobile phones, TETRA can establish a one -to -one, one -to -numbered, number of connections. Supports both the air interface encryption and the end -to -end encryption. [4]
TETRA uses a time -divided polygon (TDMA) and has four user channels and 25 carriers in one wireless carrier. You can use both points, two points and point two multi -points. Digital data transmission at low data rates is also included in the standard.
TETRA Mobile Station (MS) can communicate using a trunk mode operation (TMO) using a direct mode operation (DMO) or a TETRA base station (TBS) and a TMO using a management infrastructure (SWMI). DMO not only allows direct communication in situations where network coverage is not available, but may also use one or more TETRA terminal sequences as relays. This function is called DMO gateway (from DMO to TMO) or DMO repeater (from DMO to DMO). In an emergency, this feature allows direct communication in an area with a poor underground or in a poor coverage.
The TETRA system supports several types of data communication in addition to voice and dispatch service. With status message Short data service (SDS) is provided via the main control channel of the system, but packet exchange data or line exchange data communication uses a specially assigned channel.
TETRA provides terminal authentication to infrastructure and vice versa. In order to protect eavesdropping, air interface encryption and end -to -end encryption can be used.
The general operation mode is group calling mode. In this mode, simply press the button once and the user is connected to the selected calling group or dispatcher user. The terminal can function as a one -on -one transceiver, but there is no normal range limit because the call continues to use the network. Mobile phones that can act as TETRA terminals (on mobile phones) Directly connected to all double TETRA users or directly connected PSTN. Using an emergency button provided on the device allows users to send emergency signals to the dispatch and disable other activities performed at the same time.
Communication mode [ edit ]
The TETRA device can be connected directly to PSTN and can function as a mobile phone. It is often used in group call mode as a one -on -one walk. Pressing a call button allows users to connect to all other users in the group. Pressing an emergency button sends an emergency signal by a communication order, and gives priority to all other calls you are doing at that time. [5] 。
merit [ edit ]
The main advantages of TETRA for other technologies (such as GSMs) are as follows.
- The frequency used is much lower, so the range is long, and a very high level with a small number of transmitter. Geography Coverage is possible, reducing the cost of infrastructure.
- Even if you move to another network site during a voice call, communication will not be interrupted. This is a unique function that DPMR networks usually provide, and enables several fallback mode, such as the function of the base station processing local calls. The so -called “mission -critical” network can be built on all sides in TETRA, a fertilized/multiple redundant.
- If there is no network, mobile/portable can be directly shared with the channel using “direct mode” (transceiver mode).
- Gateway mode-A single mobile connected to the network can function as another mobile relay outside the infrastructure range. Unlike the analog radio system, there is no need for a dedicated transponder system to realize this function.
- TETRA also provides a point -to -point function not provided by the conventional analog emergency service radio system. As a result, the user can use a one -on -one trunk “wireless” link between the sets without the need to directly involve the control room operator/dispatcher.
- Unlike celluler technologies (one -on -one) connecting a single subcliver to one subclan, TETRA has been built to run one -to -one, one -on -one, and multi -to -multi -to -multi -to -multi -to -multi -converses. These operation modes are directly related to public safety and expert users.
- The quick development (transpostable) network solution can be used for disaster relief and temporary capacity provisioning.
- Network solutions can be used for both reliable line exchange (telephone -like) architectures and flat IP architectures with software (software) switches.
For details TETRA Association It can be obtained from (previous TETRA MOU). The standard can be downloaded for free from ETSI.
The main drawbacks are as follows.
- A linear amplifier is required to meet the strict RF specifications that can coexist with other wireless services.
- In the latest standard, data transfer is slow.
Both options can use 1-4 time slots. Different implementations include one, both, or one of the previous connection functions, and one time slot or higher. These rates are superficially faster than DMR, DPMR, and P25, which can be used. The latest version of the standard is the Kbit / S KHz channel with 25 KBIT / S KHz or up to 691.2 expansion 150 supporting 115.2. In order to overcome the limit, many software vendors have begun to consider hybrid solutions that use TETRA for important signaling and have 3G / LTE for large -scale data synchronization and transfer of images and videos. [6]
How to use TETRA [ edit ]
The TETRA system is used in the following countries in public divisions. Only the installation of the TETRA network infrastructure is listed. TETRA is an open standard, and each of these networks can be used by freely combining various suppliers TETRA mobile devices.
Technical details [ edit ]
For the modulation TETRA, the usage differential shift keying keying keying. The symbol (Bo) rate is 18,000 symbols per second, and each symbol is mapped to 2 bits, resulting in 36,000 bit/second.
Since the form of the phase shift keying is used to send data during each burst, it seems reasonable to expect that the transmission power is constant. But not. This is because the side wave band, which is basically repeated in the main carrier modulation, is filtered with a sharp filter so that the unnecessary spectrum is not exhausted. This is why a amplitude modulation occurs, which requires a linear amplifier. The ratio of peak -to -average (RMS) power of the result is 3.65 db. If a nonlinear amplifier is used, the side band will appear again, causing interference with the adjacent channel. The commonly used techniques to realize the necessary linearness include a decarcula loop and a adaptive pre -dystros.
The base station is usually transmitted from various mobile frequencies at various carrier frequencies and (at the same time) receiving (at the same time). Therefore, the TETRA system is a frequency division multi -centin (FDD) system. TETRA also uses FDMA / TDMA (see above) like GSM. Mobile is usually sent only in 1 slot/ 4 and receives in 1 slot/ 4 (not 1 slot/ 8 of GSM).
TETRA’s audio signal is sampled at 8kHz, then Alternative code excitation line prediction Compressed with a vocoder using (acelp). This creates a 4.567 data stream. Kilobit/second. This data stream is an error protection encoded before sending, and can be decoded correctly with noise (incorrect) (incorrect) channels. The data rate after coding is 7.2, a kilobit/second. 17/18 Capacity of a single traffic slot when using a frame.
One slot consists of 255 available symbols, and the remaining time is exhausted by synchronous sequence and on/off. One flame Is composed of four slots, Multi -frame (The duration is 1.02 seconds) consists of 18 frames. There is also a hyper frame, but is mainly used to provide synchronization with encryption algorithm.
Downlinks (that are, base stations output) are usually continuous transmissions that are composed of specific communications with mobile, synchronization, or other general broadcasts. Usually all slots Idol (Continuous mode) is buried by burst. The system uses 18 frames per second, only 17 of them are used for traffic channels, and the 18th frame is reserved for signaling, short data service messages (such as GSM SMS) or synchronization. The TETRA frame structure (17.65 frame/second) consists of 18,000 symbols/seconds. 255 symbol/slot; 4 slots/frames, 17 Be perceived This is the cause of “amplitude modulation”. Hz is especially noticeable in mobile/ portable that only sends in 1 slot/ 4. They use the remaining three slots to switch the frequency, receive bursts from the base station after two slots, and return to the transmission frequency (TDMA).
Wireless frequency [ edit ]
| number | Frequency pair (MHz) | |
|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | Band 2 | |
| Emergency system | ||
| first | 380〜383 | 390〜393 |
| 2 | 383〜385 | 393〜395 |
| Citizen system | ||
| first | 410〜420 | 420〜430 |
| 2 | 870–876 | 915〜921 |
| 3 | 450〜460 | 460〜470 |
| 4 | 385〜390 | 395〜399.9 |
| country | allocation | Frequency pair (MHz) |
|---|---|---|
| France | Folk/folk people | 410〜430 |
| Emergency service | 380〜400 | |
| Belgium | Emergency service/civilian | 380〜386.5、390〜396.5 |
| Commercial | 410〜420 | |
| Netherlands | Emergency service | 380-386.5、390-396.5 |
| Private/Commercial | 410〜430 | |
| Germany | Emergency service | In the case of DMO, 380-385, 390-395, 406-410 |
| Ireland [7] | Folk/folk people | 385〜389.9、395〜399.9 |
| Emergency service | 380〜385、390〜395 | |
| Italy | Emergency service/army | 380〜390 |
| Folk/folk people | 462 | |
| Norway [8] | Emergency service | 380〜385、390〜395、406.1〜426、870〜8766666 |
| South Africa | Emergency services, public works | 420-423 |
| U.K. | Air wave | 390.0125〜394.9875、380.0125〜384.9875 |
| Airradio | 454、464、460 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 350〜370、380〜395、385〜399.99、410〜430、450、470、870〜9212121212121 |
Air interface encryption [ edit ]
TETRA Air interface to provide confidentiality TETRA encryption algorithm (TEA) It is encrypted using one of the ciphers. Cryptography provides confidentiality (protection from eavesdropping) and signal protection.
Currently, four different encryptions are defined. Do not confuse these TEA ciphers with the block code Tiny Encryption Algorithm. TEA cipher may be used depending on export and use restrictions. There are few details published for these proprietary ciphers. Ries [9] In the early design document of TETRA, it states that encryption must be made in stream code due to the characteristics of not propagating transmission errors. Parkinson [ten] Later, this was confirmed that the TEA was a stream code using a 80 -bit key. Tea1 and Tea4 are Basic level It provides security and aims for commercial use. [11] The Tea2 cipher is limited to European public security institutions. The Tea3 cipher is suitable for situations where TEA2 is suitable but not available. [twelfth]
Additional Information [ edit ]
- Ground Trunk Radio (TETRA); Voice and Data (V + D); Part 7: Security [13]
Selection of cells [ edit ]
Re -selection (or handover) of cells in the image [ edit ]

This first expression shows the place where the low -speed re -elected value (SRT), the high -speed re -selection value (FRT), and the excess parameters are likely to be the most likely parameters. These are represented by the attenuated wireless carrier as the distance from the TETRA base station increases.
From this figure, these SRT and FRT trigger points are associated with the attenuated wireless signal intensity of each cell carrier. The threshold value is performed on time the cell re -selection procedure is placed on time, and the continuity of the ongoing communication call is guaranteed.
Selection of the first cell [ edit ]
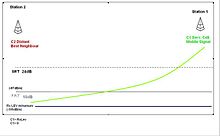
The following figure shows the location of the initial selection of the predetermined TETRA wireless cell. The first cell selection is performed by the MLE and Mac procedure. When a cell selection is performed and the possible registration is executed, Mobile bureau (MS) says that it is connected to the cell. Mobile can first select an appropriate cell with a positive C1 value. In other words, the receiving signal level is access Parameter Minimum reception level It is higher.
In the first cell selection procedure, MS can ensure that the down link data can be decoded (that is, with the main control channel/ MCCH), and a cell with a high probability of uplink communication. The minimum requirements to be satisfied are C1> 0. Access to the network requires a successful cell selection.
When the mobile switch is turned on, the mobile switches one initial cell selection of the base station. This shows the initial exchange when active.
- See En 300 392 2 16.3.1. Activation and control of the base MLE service
- Note 18.5.12 Small RX access level
The minimum reception level information element shows the minimum receiving signal level required for SWMI of any cell or adjacent cell, as defined in Table 18.24.
Improvement of cells [ edit ]

The following figure shows a specific TETRA wireless cell Give up the possibility ( give up ) It indicates a place to be. Serving cells are abandoned in the following cases. C1 of service cells is less than the value defined by the wireless network parameteracell re -selected parameters and high -speed re -selection values for 5 seconds, and is defined by the re -selection parameter of the C1 or C2 wireless network parameteracel of the adjacent cell. Only the value of 5 seconds exceeds the service cell C1.
Available cells [ edit ]
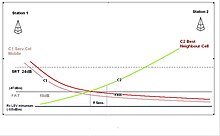
The following figure shows where the specific TETRA wireless cell Available It indicates whether it will be. If the cell has a sufficient quality downlink wireless connection, the adjacent cell will be wireless.
To declare that the radio of the adjacent cell is available, it is necessary to meet the following conditions: The pass loss parameter C1 or C2 of the adjacent cell is larger than the total of the high -speed re -selection and high -speed re -selections in 5 seconds, and the service level provided by the adjacent cell is from the service level of the service cell. Also expensive. Unless MM demands cell re -selection, cell re -selection will not succeed within the past 15 seconds. MS-MLE checks the standard for service abandonment every time a scan or surveillance is scan or monitored.
Under the following conditions, MS evaluates the adjacent cell to a higher service level than the current service cell.
- The MS subscriber class is supported by the adjacent cell, but is not supported by serving cells.
- The adjacent cell is a priority cell, and the service cell is not.
- The adjacent cell supports services that are not supported by service cells (that is, TETRA standard sounds, packet data, or encryption), and MS requires that the service is available.
- The cell service level indicates that the load on the adjacent cell is lower than the service cell.
Abandoned cells [ edit ]

The following figure shows a specific TETRA wireless cell Give up the possibility ( give up ) It indicates a place to be. Serving cells are abandoned in the following cases. C1 of service cells is less than the value defined by the wireless network parameteracell re -selected parameters and high -speed re -selection values for 5 seconds, and is defined by the re -selection parameter of the C1 or C2 wireless network parameteracel of the adjacent cell. Only the value of 5 seconds exceeds the service cell C1.
Unless mobility management (mm) request cell re -selection, cell re -selection will not succeed within the past 15 seconds. MS-MLE checks the standard for service abandonment every time a scan or surveillance is scan or monitored.
Wireless downlink disorder [ edit ]
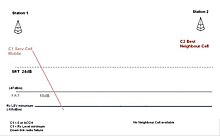
If you violate the FRT sculpture, MS abandoned (or abandoned) the service, at least usable It is essential to get another cell of quality. In other words, the mobile station recognizes that the wireless signal is rapidly attenuated, and it is necessary to quickly select the cell before the communication ends due to a wireless link failure. If the wireless signal of the mobile station violates the minimum reception level, the wireless will disappear in the position of maintaining acceptable communication for users and the wireless link will be disconnected.
Wireless link failure: (C1 <0). If you use the recommended value, this is less than -105 DBM At the service cell level It is filled. Next, the cell re -selection procedure is active to find an appropriate wireless base station.
| coverage | Parameter | Distance (km) | Types of communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| city | <4 | <8 | Pedestrian/metro |
| Suburb | 10〜18 | 20〜36 | Bus/train |
| country | 18〜31 | 36〜62 | Regional train |
| During the broadcast | > 32 | > 64 | During flight |
Mammachin interface (MMI) [ edit ]
Virtual MMI for wireless terminals [ edit ]
Java (Java Me / CLDC) -based technology, a specific TETRA wireless device, provides end users the necessary communication rights to play a short -term assignment.
For mobility, flexibility, and evolution capacity, the Faculty of Wireless Engineering of Public Transportation uses an open source, a Java language specification managed by SUN, and a related work group, Transport application tool kit Selected to create.
Tetra MMI [ edit ]
In the acquisition of the service, a different certified agent establishes communication channels between different services by calling a service ID without the full knowledge of ISID, GSSI, or other TETRA -related communication recording. Is allowed. The acquisition of the service was connected to the TETRA core network Communications intensive service or Roll allocation server It is managed through.
In summary, the purpose of TETRA MMI is as follows.
- Any agent during the exercise can use any wireless terminal without restrictions on materials.
- Providing specific transportation application software to end user agents (acquiring services, fraud, and aggression).
this Transport application tool kit Will be used normally using TETRA communication technology, and guarantees the future public transport application requirements described later.
home ( Main ) The menu presents three possibilities to the end user.
- Acquisition of service,
- Status SDS,
- End user parameter.
Acquisition of services Provides a means of virtually personalizing the end user to a specific wireless terminal and TETRA network while protecting the terminals possessed by the end user.
Status SDS provides end users with the mechanism that generates 440. A member of a member of the same (dynamic or static) short sub -sliver ID (GSSI) or a specific individual short sub -sliver ID (ISSI) period (specific for 1 hour, every morning patrol or assigned assignment. short period). The advantage is that each end user can connect to a specific terminal and group in a short time without the need for a large reconstruction tools with a wireless software programming tool. Similarly, the attack function functions, but has a higher tone frequency (880 Hz) and a more rapid repetitive property, emphasizing the urgency of the alert.
[ Parameter ] The tab is targeted by terminal end users (programmed in advance) These or Gss ) We provide important means to make the address communication number in advance. Using this pre -programmed address number, end users are addressed wireless terminals or Roll allocation server In contact with, in the group, or requested a service acquisition, it is pre -treated, and eventually communicates with a dedicated server. Dispatched through the TETRA core network. This simplifies the reconfiguration or recycling configuration process, enabling short assignment flexibility.
The parameter tab also provides a way to select from the tone selected in advance to match the work group requirements for the purpose of fraud and attack warning. With the Transport Application Software Toolkit, you can select any key that can be used from the key pad and function as an aggression or an illegal quick key. For fraud and aggression quick keys, it is recommended to use asterisks and hash keys, respectively. For fraud and aggressive tones, it is also recommended to use 440 Hz low -speed repetitive tones (blank space 500 milliseconds) and 880 Hz high -speed repetition (blank space 250 milliseconds). The tone options are as follows. Hz, 620 Hz, 880 Hz, and 1060 Hz.
Parameter On the page support or help There is a menu, and the last tab in the parameter briefly describes the history of the tool kit version and the history of the Transport Application Toolkit to date.
TETRA Extended Data Service (TEDS) [ edit ]
TETRA Association has developed TEDS standard in cooperation with ETSI. This is a wide band data solution that extends TETRA to significantly improve data capacity and throughput. In addition to what TETRA is provided, TEDS is 150 kHz from 25 to KHz from 25 to KHz to KHz. The first implementation of TEDS is performed on the existing TETRA wireless spectrum, and perhaps the 50 kHz channel bandwidth enables the same coverage footprint of voice and TEDS services. The performance of TEDS is optimized for wide -band data rates, wide -area coverage, and spectrum efficiency. [14]
With the advancement of DSP technology, a multi -carrier transmission standard that adopted QAM modulation was introduced. WiMAX, Wi-Fi, and Teds standards are part of this family.
- JSR-118 ;
- Mobile Information Device Profile, JSR-37;
- Wireless messaging API, JSR120;
- Connected restricted device configuration, JSR-139;
- JTWI-185, technology for the wireless industry.
Comparison of TETRA and Project 25 [ edit ]
Project 25 and TETRA are used for public safety radio networks and private wireless networks around the world, but there are several differences between technical features and capacity. [15] [16] [17]
- TETRA: High spectrum efficiency (25 4 -time slot) KHz: 4 communication channels per 25, which is optimized for areas with high population density, efficient use of spectrum). Suitable for areas with high population density and supports full duplicate audio, data and messaging. However, it cannot be used in Simal Cast and VHF bands. However, a specific vendor has introduced SimulCast and VHF on the TETRA platform. 。
- P25: The population density is low, and it is optimized to cover a wider area, supporting simultaneous broadcasting. However, it is limited to data support. (Phase 1 P25 wireless system operates in 12.5 KHz analog, digital or mixed mode, and P25 phase II are 12.5 KHz channel that uses a two -time slot TDMA structure with 12.5.
Currently, the P25 is deployed in more than 53 countries, and TETRA is deployed in more than 114 countries.
references [ edit ]
- ^ Data to be verified
External link [ edit ]
Recent Comments