2018 Texas elections – Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The 2018 general election was held in the U.S. state of Texas on November 6, 2018. All of Texas’s executive officers were up for election as well as a United States Senate seat, and all of Texas’s thirty-six seats in the United States House of Representatives. The Republican and Democratic Parties nominated their candidates by primaries held March 6, 2018. Convention Parties nominated their candidates at a series of conventions. County Conventions held March 17, 2018, District Conventions held March 24, 2018, and a State Convention held April 14, 2018.[1] At the present time there is only one Convention Party in Texas, that is the Libertarian Party. Other parties may seek to achieve ballot access.[2]
Turnout in the November general election reached historic levels, rivaling turnout in a presidential election.[3] While the Republican Party won every statewide position, the margin of victory was narrower than previous elections.[4][5][6]
United States Senate[edit]
Democratic U.S. Representative Beto O’Rourke and Libertarian candidate Neal Dikeman challenged U.S. Senator Ted Cruz for re-election. Cruz narrowly defeated O’Rourke by 2.6%.
United States House of Representatives[edit]
All of Texas’s thirty-six seats in the United States House of Representatives were up for election in 2018.[7] No open seats changed hands, but two Republican incumbents lost to Democrats.
Governor[edit]
Incumbent governor Greg Abbott ran for a second term. He was first elected in 2014 after serving twelve years as Texas Attorney General, and he succeeded Rick Perry as governor.
Abbott won the March 20, 2018, Republican primary, while Lupe Valdez won the Democratic runoff against Andrew White, becoming the first Latina nominated by a major party for statewide office in Texas.
Libertarian Mark Tippetts also ran against Abbott. Tippetts defeated Kathie Glass, Patrick “Not Governor” Smith, and Kory Watkins at the party convention to earn his nomination.[8]
Lieutenant governor[edit]
On January 9, 2017, the day before the 85th Texas Legislature began its session, incumbent Republican lieutenant governor Dan Patrick announced he would run for re-election in 2018.[9] He stated his early announcement was in order to dispel rumors of a primary challenge to Governor Greg Abbott or U.S. Senator Ted Cruz.[9]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
- Mike Collier, businessman, finance Chair of the Texas Democratic Party, and nominee for Comptroller in 2014[13]
- Michael Cooper, businessman, community leader, and pastor[14]
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
- Kerry Douglas McKennon[16]
General election[edit]
Polling[edit]
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Dan Patrick (R) |
Mike Collier (D) |
Kerry McKennon (L) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dixie Strategies | September 6–7, 2018 | 519 | ± 4.3% | 45% | 39% | 2% | – | 14% |
| Texas Lyceum | July 9–26, 2018 | 441 | ± 4.7% | 39% | 29% | 4% | – | 28% |
| Gravis Marketing | July 3–7, 2018 | 602 | ± 4.0% | 46% | 44% | – | – | 10% |
| UoT/Texas Tribune | June 8–17, 2018 | 1,200 | ± 2.83% | 37% | 31% | 4% | 5% | 23% |
Results[edit]
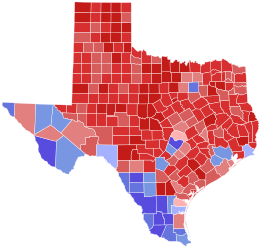
- Patrick: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90%
Collier: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80%
Attorney general[edit]
Incumbent Republican attorney general Ken Paxton ran for re-election to a second term.[7]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
General election[edit]
Endorsements[edit]
Ken Paxton
- Presidents of the United States
- Organizations
Polling[edit]
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Ken Paxton (R) |
Justin Nelson (D) |
Michael Ray Harris (L) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dixie Strategies | September 6–7, 2018 | 519 | ± 4.3% | 45% | 39% | 2% | – | 15% |
| Texas Lyceum | July 9–26, 2018 | 441 | ± 4.7% | 35% | 25% | 4% | – | 37% |
| Gravis Marketing | July 3–7, 2018 | 602 | ± 4.0% | 45% | 41% | – | – | 14% |
| UoT/Texas Tribune | June 8–17, 2018 | 1,200 | ± 2.83% | 32% | 31% | 6% | 4% | 26% |
| Baselice & Associates (R-TLRPAC) | May 21–28, 2018 | – | – | 45% | 33% | – | – | – |
Results[edit]
Comptroller of Public Accounts[edit]
Incumbent Republican Comptroller Glenn Hegar ran for re-election to a second term.[7]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Commissioner of the General Land Office[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
General election[edit]
Endorsements[edit]
George P. Bush
- Presidents of the United States
Polling[edit]
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
George P. Bush (R) |
Miguel Suazo (D) |
Matt Pina (L) |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dixie Strategies | September 6–7, 2018 | 519 | ± 4.3% | 46% | 30% | 3% | – | 22% |
Results[edit]
Commissioner of Agriculture[edit]
Incumbent Republican Commissioner Sid Miller ran for re-election to a second term.[7]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Texas Railroad Commissioner[edit]
Incumbent Republican Commissioner Christi Craddick ran for re-election to a second six-year term.[7]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
- Roman McAllen, historic preservation officer[36]
- Chris Spellmon
Results[edit]
Libertarian state convention[edit]
Candidates[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Supreme Court of Texas[edit]
Justice, Place 2 election[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Justice, Place 4 election[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
- John Devine, incumbent Associate Justice of the Texas Supreme Court
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Justice, Place 6 election[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
- Jeff Brown, incumbent Associate Justice of the Texas Supreme Court
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Texas Court of Criminal Appeals[edit]
Presiding Judge election[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Judge, Place 7 election[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Judge, Place 8[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Candidates[edit]
Results[edit]
General election[edit]
Results[edit]
Texas State Board of Education[edit]
Member, District 2[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Member, District 3[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Member, District 4[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Member, District 7[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Member, District 11[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Member, District 12[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
First round[edit]
Malone-Miller withdrew after the first round, eliminating the need for a runoff.
General election[edit]
Member, District 13[edit]
Republican primary[edit]
Democratic primary[edit]
General election[edit]
Texas Legislature[edit]
Every seat in the Texas House of Representatives and about half of the seats in the Texas Senate were up for election.
Texas Senate[edit]

Republican Hold
Democratic Hold
Republican Gain
Democratic Gain
Texas House of Representatives[edit]

Republican Hold
Democratic Hold
Democratic Gain
Texas Courts of Appeals[edit]
|
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2019)
|
Local trial courts[edit]
|
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2019)
|
School boards[edit]
|
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2019)
|
Municipal[edit]
|
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2019)
|
Controversies[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2018)
|
References[edit]
- ^ “Important Dates for the Party Conventions, Primary Elections and General Election”. www.sos.state.tx.us.
- ^ “Nominee of Libertarian or Green Party in 2018”. www.sos.state.tx.us.
- ^ Wang, Elbert (November 7, 2017). “Look up Texas midterm turnout in your county against historic numbers”. The Texas Tribune. Retrieved November 7, 2017.
- ^ Platoff, Emma (November 7, 2017). “Texas Democrats were aiming for historic wins in 2018. What they got instead was hope for 2020”. The Texas Tribune. Retrieved November 7, 2017.
- ^ Zdun, Matt; Collier, Kiah (November 7, 2017). “Gov. Greg Abbott clinches second term as GOP wins closest statewide races in 20 years”. The Texas Tribune. Retrieved November 7, 2017.
- ^ Platoff, Emma (November 7, 2017). “Four top takeaways from the 2018 Texas midterm elections”. The Texas Tribune. Retrieved November 7, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Executive Branch Archived 2011-06-29 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 23-October-2008
- ^ “Texas Libertarians nominate Mark Tippetts for governor | Libertarian Party”. Libertarian Party. 2018-04-18. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- ^ a b Whitely, Jason (January 9, 2017). “Lt. Gov. Patrick Announces Re-Election Campaign”. WFAA. Retrieved January 10, 2017.
- ^ “Milder to Challenge Dan Patrick”. The Amarillo Pioneer. Retrieved 2017-12-04.
- ^ “Austin native Scott Milder announces bid for Lieutenant Governor”. Retrieved 2017-12-04.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o “2018 Republican Party Primary Election – Race Summary Report”. Office of Texas Secretary of State.
- ^ “Mike Collier is the only challenger to Texas’ GOP-led government”. 3 June 2017.
- ^ “Beaumont pastor announces bid for lieutenant governor”. News6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p “2018 Democratic Party Primary Election – Race Summary Report”. Office of Texas Secretary of State.
- ^ a b c d “2018 Candidates”. lptexas.org. Archived from the original on December 22, 2017. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k “2018 General Election – Race Summary Report”. Office of Texas Secretary of State.
- ^ “Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton draws first Democratic challenger for 2018”. texastribune.org. Retrieved January 16, 2018.
- ^ “2018 Candidates”. lptexas.org. Archived from the original on September 9, 2018. Retrieved September 9, 2018.
- ^ “President Trump endorsed Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton”. RAGA. May 7, 2018.
- ^ “NRA Endorses Ken Paxton for Attorney General”. NRA-ILA. September 7, 2018.
- ^ “Open Carry Texas Endorses Attorney General Ken Paxton”. AmmoLand.com. September 5, 2018.
- ^ “Texas Comptroller Glenn Hegar and Democratic challenger Joi Chevalier on why they deserve your vote”. The Texas Tribune. 2018-10-25. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- ^ vote4sanders.com
- ^ Weissert, Will (June 19, 2017). “George P Bush seeks re-election as Texas land commissioner”. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on June 19, 2017. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- ^ Tribe, Kristen (March 29, 2017). “Edwards pursues state office”. Wise County Messenger. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ Tribe, Kristen (June 4, 2017). “Edwards starts signature drive for place on ballot”. Wise County Messenger. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ “Trump Endorses Top Texas Republicans”. www.governing.com.
- ^ “Profile: Rick Range, Republican for Texas Land Commissioner”. The Amarillo Pioneer. Retrieved 2018-11-11.
- ^ “George Bush on Twitter”.
- ^ “Donald J. Trump on Twitter”.
- ^ “Austin Lobbyist to Challenge Sid Miller”. The Amarillo Pioneer. Retrieved 2017-12-04.
- ^ “Sid Miller Announces Re-election Campaign for Texas Agriculture Commissioner”. Texas Insider. 2017-11-13. Retrieved 2017-11-20.
- ^ “Sid Miller announces reelection bid”. Dallas Voice. 2017-11-08. Retrieved 2017-11-20.
- ^ Coyne, Christin (May 19, 2017). “Former WISD trustee Olson seeks office”. Weatherford Democrat. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ Heinkel-Wolfe, Peggy (July 5, 2017). “McAllen announces run for Texas Railroad Commission”. Denton Record-Chronicle. Retrieved July 18, 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Platoff, Emma (November 9, 2017). “In race against Texas judge Sharon Keller, Republican highlighting infamous death row call”. The Texas Tribune.
- ^ a b c McCullough, Jolie (February 28, 2018). “Three Republicans vie for Texas Court of Criminal Appeals seat, replacing death penalty critic”. The Texas Tribune.
External links[edit]
- Official Lieutenant Governor campaign websites
- Official Attorney General campaign websites
- Official Comptroller of Public Accounts campaign websites
- Official Commissioner of the General Land Office campaign websites
- Official Commissioner of Agriculture campaign websites
- Official Railroad Commissioner campaign websites
- Official Supreme Court of Texas, Place 2 campaign websites
- Official Supreme Court of Texas, Place 4 campaign websites
- Official Supreme Court of Texas, Place 6 campaign websites
Recent Comments