Entropic value at risk – Wikipedia
In financial mathematics and stochastic optimization, the concept of risk measure is used to quantify the risk involved in a random outcome or risk position. Many risk measures have hitherto been proposed, each having certain characteristics. The entropic value at risk (EVaR) is a coherent risk measure introduced by Ahmadi-Javid,[1][2] which is an upper bound for the value at risk (VaR) and the conditional value at risk (CVaR), obtained from the Chernoff inequality. The EVaR can also be represented by using the concept of relative entropy. Because of its connection with the VaR and the relative entropy, this risk measure is called “entropic value at risk”. The EVaR was developed to tackle some computational inefficiencies[clarification needed] of the CVaR. Getting inspiration from the dual representation of the EVaR, Ahmadi-Javid[1][2] developed a wide class of coherent risk measures, called g-entropic risk measures. Both the CVaR and the EVaR are members of this class.
Definition[edit]
Let
be a probability space with
a set of all simple events,
a
-algebra of subsets of
and
a probability measure on
. Let
be a random variable and
be the set of all Borel measurable functions
whose moment-generating function
exists for all
. The entropic value at risk (EVaR) of
with confidence level
is defined as follows:
-
(1)
In finance, the random variable
in the above equation, is used to model the losses of a portfolio.
Consider the Chernoff inequality
-
(2)
Solving the equation
for
results in
By considering the equation (1), we see that
- is the entropic risk measure or exponential premium, which is a concept used in finance and insurance, respectively.
Let
be the set of all Borel measurable functions
whose moment-generating function
exists for all
. The dual representation (or robust representation) of the EVaR is as follows:
-
(3)
where
and
is a set of probability measures on
with
. Note that
is the relative entropy of
with respect to
also called the Kullback–Leibler divergence. The dual representation of the EVaR discloses the reason behind its naming.
Properties[edit]
- The EVaR is a coherent risk measure.
- The moment-generating function can be represented by the EVaR: for all and
(4)
-
- The entropic risk measure with parameter can be represented by means of the EVaR: for all and
(5)
- The EVaR with confidence level is the tightest possible upper bound that can be obtained from the Chernoff inequality for the VaR and the CVaR with confidence level ;
-
-
(6)
-
- The following inequality holds for the EVaR:
-
-
(7)
-
- where is the expected value of and is the essential supremum of , i.e., . So do hold and .
Examples[edit]
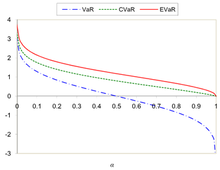 Comparing the VaR, CVaR and EVaR for the standard normal distribution
Comparing the VaR, CVaR and EVaR for the standard normal distribution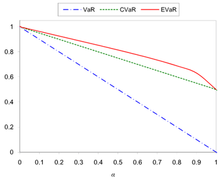 Comparing the VaR, CVaR and EVaR for the uniform distribution over the interval (0,1)
Comparing the VaR, CVaR and EVaR for the uniform distribution over the interval (0,1)For
-
(8)
For
-
(9)
Figures 1 and 2 show the comparing of the VaR, CVaR and EVaR for
and
.
Optimization[edit]
Let
be a risk measure. Consider the optimization problem
-
(10)
where
is an
-dimensional real decision vector,
is an
-dimensional real random vector with a known probability distribution and the function
is a Borel measurable function for all values
If
then the optimization problem (10) turns into:
-
(11)
Let
be the support of the random vector
If
is convex for all
, then the objective function of the problem (11) is also convex. If
has the form
-
(12)
and
are independent random variables in
, then (11) becomes
-
(13)
which is computationally tractable. But for this case, if one uses the CVaR in problem (10), then the resulting problem becomes as follows:
-
(14)
It can be shown that by increasing the dimension of
, problem (14) is computationally intractable even for simple cases. For example, assume that
are independent discrete random variables that take
distinct values. For fixed values of
and
the complexity of computing the objective function given in problem (13) is of order
while the computing time for the objective function of problem (14) is of order
. For illustration, assume that
and the summation of two numbers takes
seconds. For computing the objective function of problem (14) one needs about
years, whereas the evaluation of objective function of problem (13) takes about
seconds. This shows that formulation with the EVaR outperforms the formulation with the CVaR (see [2] for more details).
Generalization (g-entropic risk measures)[edit]
Drawing inspiration from the dual representation of the EVaR given in (3), one can define a wide class of information-theoretic coherent risk measures, which are introduced in.[1][2] Let
be a convex proper function with
and
be a non-negative number. The
-entropic risk measure with divergence level
is defined as
-
(15)
where
in which
is the generalized relative entropy of
with respect to
. A primal representation of the class of
-entropic risk measures can be obtained as follows:
-
(16)
where
is the conjugate of
. By considering
-
(17)
with
and
, the EVaR formula can be deduced. The CVaR is also a
-entropic risk measure, which can be obtained from (16) by setting
-
(18)
with
and
(see [1][3] for more details).
For more results on
-entropic risk measures see.[4]
Disciplined Convex Programming Framework[edit]
The disciplined convex programming framework of sample EVaR was proposed by Cajas[5] and has the following form:
-
(19)
where
,
and
are variables;
is an exponential cone;[6] and
is the number of observations. If we define
as the vector of weights for
assets,
the matrix of returns and
the mean vector of assets, we can posed the minimization of the expected EVaR given a level of expected portfolio return
as follows.
-
(20)
Applying the disciplined convex programming framework of EVaR to uncompounded cumulative returns distribution, Cajas[5] proposed the entropic drawdown at risk(EDaR) optimization problem. We can posed the minimization of the expected EDaR given a level of expected return
as follows:
-
(21)
where
is a variable that represent the uncompounded cumulative returns of portfolio and
is the matrix of uncompounded cumulative returns of assets.
For other problems like risk parity, maximization of return/risk ratio or constraints on maximum risk levels for EVaR and EDaR, you can see [5] for more details.
The advantage of model EVaR and EDaR using a disciplined convex programming framework, is that we can use softwares like CVXPY [7] or MOSEK[8] to model this portfolio optimization problems. EVaR and EDaR are implemented in the python package Riskfolio-Lib.[9]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
 be a probability space with
be a probability space with  a set of all simple events,
a set of all simple events,  a
a  -algebra of subsets of
-algebra of subsets of  a probability measure on
a probability measure on  be a random variable and
be a random variable and  be the set of all Borel measurable functions
be the set of all Borel measurable functions  whose moment-generating function
whose moment-generating function  exists for all
exists for all  . The entropic value at risk (EVaR) of
. The entropic value at risk (EVaR) of  with confidence level
with confidence level  is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:

 in the above equation, is used to model the losses of a portfolio.
in the above equation, is used to model the losses of a portfolio.

 for
for  results in
results in



 be the set of all Borel measurable functions
be the set of all Borel measurable functions  . The dual representation (or robust representation) of the EVaR is as follows:
. The dual representation (or robust representation) of the EVaR is as follows:

 and
and  is a set of probability measures on
is a set of probability measures on  with
with  . Note that
. Note that

 with respect to
with respect to  also called the Kullback–Leibler divergence. The dual representation of the EVaR discloses the reason behind its naming.
also called the Kullback–Leibler divergence. The dual representation of the EVaR discloses the reason behind its naming.
















 and
and  .
.
 be a risk measure. Consider the optimization problem
be a risk measure. Consider the optimization problem

 is an
is an  -dimensional real decision vector,
-dimensional real decision vector,  is an
is an  -dimensional real random vector with a known probability distribution and the function
-dimensional real random vector with a known probability distribution and the function  is a Borel measurable function for all values
is a Borel measurable function for all values  If
If  then the optimization problem (10) turns into:
then the optimization problem (10) turns into:

 be the support of the random vector
be the support of the random vector  If
If  is convex for all
is convex for all  , then the objective function of the problem (11) is also convex. If
, then the objective function of the problem (11) is also convex. If  has the form
has the form

 are independent random variables in
are independent random variables in 
![{displaystyle min _{{boldsymbol {w}}in {boldsymbol {W}},tin mathbb {R} }leftlbrace t+{frac {1}{alpha }}{text{E}}left[g_{0}({boldsymbol {w}})+sum _{i=1}^{m}g_{i}({boldsymbol {w}})psi _{i}-tright]_{+}rightrbrace .}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8fd60d85fb67797f3d44f5741f97314be2072986)
 , problem (14) is computationally intractable even for simple cases. For example, assume that
, problem (14) is computationally intractable even for simple cases. For example, assume that  distinct values. For fixed values of
distinct values. For fixed values of  and
and  the complexity of computing the objective function given in problem (13) is of order
the complexity of computing the objective function given in problem (13) is of order  while the computing time for the objective function of problem (14) is of order
while the computing time for the objective function of problem (14) is of order  . For illustration, assume that
. For illustration, assume that  and the summation of two numbers takes
and the summation of two numbers takes  seconds. For computing the objective function of problem (14) one needs about
seconds. For computing the objective function of problem (14) one needs about  years, whereas the evaluation of objective function of problem (13) takes about
years, whereas the evaluation of objective function of problem (13) takes about  seconds. This shows that formulation with the EVaR outperforms the formulation with the CVaR (see [2] for more details).
seconds. This shows that formulation with the EVaR outperforms the formulation with the CVaR (see [2] for more details).
 be a convex proper function with
be a convex proper function with  and
and  be a non-negative number. The
be a non-negative number. The 
 in which
in which  is the generalized relative entropy of
is the generalized relative entropy of ![{displaystyle {text{ER}}_{g,beta }(X)=inf _{t>0,mu in mathbb {R} }leftlbrace tleft[mu +{text{E}}_{P}left(g^{*}left({frac {X}{t}}-mu +beta right)right)right]rightrbrace }”/></span></div>
</td>
<td style=](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/03980f4d09c2a5a913ca0a64866c3a747d851fd5)
 is the conjugate of
is the conjugate of 
 and
and  , the EVaR formula can be deduced. The CVaR is also a
, the EVaR formula can be deduced. The CVaR is also a 
 and
and  (see [1][3] for more details).
(see [1][3] for more details).

 and
and  are variables;
are variables;  is an exponential cone;[6] and
is an exponential cone;[6] and  is the number of observations. If we define
is the number of observations. If we define  as the vector of weights for
as the vector of weights for  assets,
assets,  the matrix of returns and
the matrix of returns and  the mean vector of assets, we can posed the minimization of the expected EVaR given a level of expected portfolio return
the mean vector of assets, we can posed the minimization of the expected EVaR given a level of expected portfolio return  as follows.
as follows.


 is a variable that represent the uncompounded cumulative returns of portfolio and
is a variable that represent the uncompounded cumulative returns of portfolio and  is the matrix of uncompounded cumulative returns of assets.
is the matrix of uncompounded cumulative returns of assets.
Recent Comments