Regions of Western Australia – Wikipedia
Designated regions of Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is divided into regions according to a number of systems.
The most common system is the WA Government division of the state into regions for economic development purposes, which comprises nine defined regions; however, there are a number of other systems, including those made for purposes of land management (such as agriculture and conservation), information gathering (such as statistical and meteorological), and election for political office.
The various different systems were defined for different purposes, and give specific boundaries, but although many of the different systems’ regions have similar names, they have different boundaries; the names and boundaries of regions can and do vary between systems.
The Regional Development Commissions Act regions[edit]
The Western Australian system of regions defined by the Government of Western Australia for purposes of economic development administration, which excludes the Perth metropolitan region, is a series of nine regions.
These nine regions were established by the Regional Development Commissions Act 1993, which defined their extents and established Regional Development Commissions to promote their economic development.[1] In defining the regions, an attempt was made to capture distinct socio-economic communities. For example, the Goldfields–Esperance region of Western Australia has an economy based heavily on mining, whereas the Wheatbelt region is economically dependent on agriculture.
| Region | Largest city | Number of LGAs (list) |
Land area | Map | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gascoyne | Carnarvon | 4 | 137,938 km2 (53,258.16 sq mi) | 
|
[2] |
| Goldfields–Esperance | Kalgoorlie | 10 | 955,276 km2 (368,834.13 sq mi) | 
|
[3] |
| Great Southern | Albany | 11 | 39,007 km2 (15,060.69 sq mi) | 
|
[4] |
| Kimberley | Broome | 4 | 424,517 km2 (163,906.93 sq mi) | 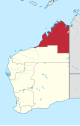
|
[5] |
| Mid West | Geraldton | 16 | 285,497 km2 (110,231.01 sq mi) | 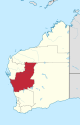
|
[6] |
| Peel | Mandurah | 5 | 6,648 km2 (2,566.81 sq mi) | 
|
[7] |
| Pilbara | Karratha | 4 | 507,896 km2 (196,099.74 sq mi) | 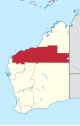
|
[8] |
| South West | Bunbury | 12 | 24,000 km2 (9,266.45 sq mi) | 
|
[9] |
| Wheatbelt | Northam | 42 | 154,862 km2 (59,792.55 sq mi) | 
|
[10] |
Inter-regional travel restrictions during COVID-19 pandemic[edit]

During the Western Australian government response to the COVID-19 pandemic, travel between regions – other than between Perth and Peel – was restricted, with police checkpoints set up at the borders. Only essential travel was allowed.[11] At some checkpoints, police were assisted by army and State Emergency Service personnel;[12] the army did not have any authority to prosecute or arrest.[13] Remote communities and some “biosecurity areas”[14] had further travel restrictions[15] due to the lack of medical facilities and number of high risk community members. Some inter-regional restrictions were lifted on 18 May,[16][14] and on 5 June all regional restrictions were removed except for remote Aboriginal communities.[17]
On 31 January 2021, after a quarantine hotel security guard in Perth tested positive, a five-day lockdown, from 6pm on 31 January until 6pm on 5 February was declared. Schools scheduled to resume on 1 February were to remain closed for another week.[18] The areas affected were: “… the whole Perth metropolitan area, the Peel region and the South West region …”[18]
Bureau of Meteorology regions[edit]
The same region names as those used by the Regional Development Commissions Act (RDCA) are incorporated into the system used by Bureau of Meteorology (BOM),[19] which uses 14 regions, so the boundaries of the two systems do not coincide. In some of the regions, the BOM designates the forecast area regions with a finer level of detail using points of the compass. Regions numbered 8 to 14 are usually known as forecast areas in the South West Land Division; coastal zones for sea forecasts are dealt with in the coastal regions of Western Australia.
South West Western Australia Fire Weather Forecast Areas[edit]
The South West Land Division has 23 fire districts.[20]
Political regions[edit]
Under Australia’s three-tiered system of government, Western Australia has four political regional schemes:
State government departmental regions[edit]
Many government departments maintain systems of regional and district breakdowns of the state for their own internal purposes.
- Department of Education[21]
- Goldfields
- Kimberley
- Midwest
- North Metro
- Pilbara
- South Metro
- Southwest
- Wheatbelt
- Department of Agriculture and Food[22]
- Northern Agricultural Region
- Rangelands Region
- Southern Agricultural Region
- Central Agricultural Region
- South West Agricultural
- Main Roads Western Australia[23]
- Kimberley
- Pilbara
- Mid-West-Gascoyne
- Goldfields-Esperance
- Wheatbelt
- Metropolitan
- Great Southern
- South-West
- Department of Water[24]
- Kimberley
- Pilbara
- Mid West Gascoyne
- Goldfields
- Swan-Avon
- Kwinana Peel
- South West
- South Coast
- Department of Fisheries[25]
Fisheries tends to separate the state into four main regions for the purpose of regulating recreational fishing:
- North Coast – Pilbara-Kimberley
- Gascoyne Coast
- West Coast
- South Coast.
- Department of Mines and Petroleum
The department produces statistical data based on the Regional Development Commissions Act regionalisation schema
Since the creation of the Department of Industry and Resources some rationalisation of mines administration has occurred, however the mineral fields and boundaries remain the same as when established.[26]
- Department of Planning, Lands and Heritage / Western Australian Planning Commission
There are three regions with regional planning schemes, covering only a small part of the state:[27]
- Metropolitan Region Scheme (Perth)
- Peel Region Scheme
- Greater Bunbury Region Scheme
- Department of Fire and Emergency Services[28]
- Kimberley
- Pilbara
- Mid West Gascoyne
- Goldfields
- Great Southern
- Kwinana Peel
- South West
- Lower South West
- Metropolitan
- Department of Health[29][30]
- Kimberley
- Pilbara
- Midwest
- Goldfields
- Wheatbelt
- South West
- Great Southern
- North Metropolitan
- South Metropolitan
- East Metropolitan
Natural and land management[edit]
See also Category:Biogeography of Western Australia
There are a number of regionalisations that attempt to provide a regionalisation based on natural features. The best known of these are the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) regions, and the World Wildlife Fund’s Ecoregions in Australia, and the “natural regions” of John Stanley Beard, all of which are based on biogeography. Other natural regionalisations included the drainage basins and catchments of river systems, and highly specialised regionalisations dealing with such matters as geology and soil systems.
Administrative regionalisations include Landcare Districts and the Department of Agriculture’s “Land-use Zones”. However the Department of Agriculture publications – Technical Bulletins[31] – usually titled An inventory and condition report/survey… of a particular region are very specifically focused upon land systems that are based on natural features.
Land tenure[edit]
Western Australia is divided into approximately 90 land districts for cadastral purposes. There are five land divisions in Western Australia, as specified in Schedule 1 of the Land Administration Act 1997.
- Eastern Land Division
- Eucla Land Division
- Kimberley Land Division
- North-West Land Division
- South-West Land Division
Wine regions[edit]
Western Australia covers the western third of the continent, although the winemaking regions are almost entirely situated in the south-western tip of the state. It has nine regions, and five nominated subregions for wine under the geographical indications legislation as determined by the Australian Wine and Brandy Corporation.[32][33][34]
Wine regions include:[35]
- Greater Perth
- South Western Australia
Coastal regions[edit]
Western Australia has the longest coastline of any state in Australia, at 10,194 km.[36] The regions can be determined by the underlying geology, and in the case of the Bureau of Meteorology – features such as points and capes are useful indicators of coastal water forecasts.[37]
Landgate publishes touring maps that include coastal zones including:
- Batavia Coast (incorporating the area of Dongara, Geraldton, and Kalbarri)[38]
- Gascoyne Coast (Carnarvon, Coral Bay, Denham, Exmouth and the Coral Coast)
- Coral Coast (at the northern end of the Gascoyne Coast)
- Turquoise Coast north of sunset Coast and south of Batavia coast
- Sunset Coast (Perth Metropolitan beachside suburbs from Cottesloe to Yanchep)
Census and Australian Bureau of Statistics[edit]
For the purposes of statistical geography, the Australian Bureau of Statistics uses the Australian Standard Geographical Classification, a hierarchical regionalisation that divides Western Australia into statistical divisions, then statistical subdivisions, statistical local areas, and finally, census collection districts.
Statistical divisions include:[39]
- SD 505 – Perth
- SD 510 – South West
- SD 515 – Lower Great Southern
- SD 520 – Upper Great Southern
- SD 525 – Midlands
- SD 530 – South Eastern
- SD 535 – Central
- SD 540 – Pilbara
- SD 545 – Kimberley
The ABS produces regional profiles for the nine ABS statistical divisions, and the ten Development Commission[clarification needed] regions.
Cross-regional terminology[edit]
In some cases, regions have been grouped into larger areas, to describe a larger area in a single term:
- Arid Western Australia tends to be synonymous with the Eremaean province biological region relating to plants and dry conditions
- Remote Western Australia – also synonymous with Outback Western Australia – is determined by the distance and separation from the more heavily populated south west region surrounding Perth and its adjacent hinterland, and the subsequent scattered and low density populated areas towards the central east of Western Australia.
- North West Australia similarly crosses the usual regional definitions to designate an area.
- Southwest Australia may also ignore usual regional definitions.
- Nullarbor – a term with multiple meanings – covers between south east Western Australia, and far west South Australia.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
External links[edit]
Further reading[edit]
- Regions Western Australia. Perth, W.A. : Dept. of Commerce and Trade. Issue 1 (Mar./June 1998)-issue 11 (February 2002)
- Regional futures: challenges and opportunities for Western Australia’s regions: a discussion paper prepared by the Regional Development Council and the Department of Commerce and Trade. Perth, W.A. : The Council, Rev. June 1996.
- Western Australia: a statistical snapshot of the regions prepared by the Department of Commerce and Trade for the Regional Development Council. Perth: The Department., 1995.
- Western Australia tomorrow: population projections for the statistical divisions, planning regions and local government areas of Western Australia. Perth, W.A. : Western Australian Planning Commission, 2000. Population report (Western Australian Planning Commission) ; no. 4. ISBN 0-7309-9222-5
- Streetsmart Travellers Atlas of Western Australia (2006) Department of Land Information and West Australian Newspapers,9th ed. ISBN 1-921048-13-1
- Quality Publishing Australia.(2007) Roads & tracks Western Australia: campsites directory, roads and tracks, all in one Jolimont, W.A.,Quality Publishing Australia, 5th ed ISBN 1-876723-35-1
- UBD Western Australia country road atlas (2005) Macquarie Park, N.S.W.UBD, a division of Universal Publishers, 11th ed ISBN 0-7319-1587-9
Recent Comments