List of United States Army tactical truck engines
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In the late 1930s the US Army began setting requirements for custom built tactical trucks, winning designs would be built in quantity. As demand increased during WWII some standardized designs were built by other manufactures.
Most trucks had gasoline (G) engines until the early 1960s, when multifuel (M) and diesel (D) engines were introduced. Since then diesel fuel has increasingly been used, the last gasoline engine vehicles were built in 1985.
Most engines have been water-cooled with inline (I) cylinders, but V types (V) and opposed (O) engines have also been used. Three air-cooled engines were used in two very light trucks. Gasoline engines up to WWII were often valve in block design (L-head), during the war more overhead valve (ohv) engines were used, and after the war all new engines (except 1 F-head and 1 Overhead camshaft (ohc)) have been ohv. All diesel engines have ohv, they can be naturally aspired, supercharged (SC), or turbocharged (TC).
The same engines have been used in different trucks, and larger trucks often have had different engines during their service life. Because of application and evolution, the same engine often has different power ratings. Ratings are in SAE gross horsepower.
The front of an engine is the fan end, the rear is the flywheel end, right and left are as viewed from the rear, regardless of how the engine is mounted in the vehicle. Engines in the tables are water-cooled and naturally aspirated unless noted.
-
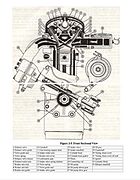
Kaiser-Jeep Tornado
(front cutaway) -

-

American Motors AV-108-4
(left rear) -

American Motors AV-108-4
(right front) -
-

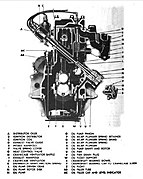
Willys MB
(left side cutaway) -

-

-

Caterpillar 3116 (left front)
-

Caterpillar 3116 (right rear)
-

-

-

-

-

Chevrolet BV-1001
(left side) -

Chevrolet BV-1001
(right side)
-

-
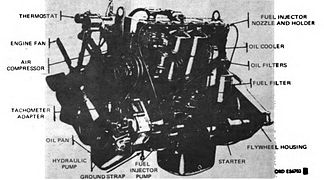
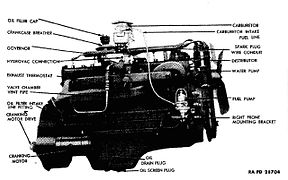
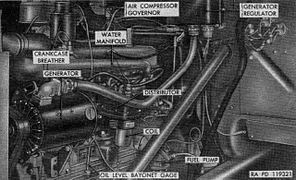
Ordnance design LDT-465
(left front) -

Ordnance design LDT-465
(right rear) -

Continental R22
(left side) -

Continental R22
(right side) -

Continental R6602
(left side) -
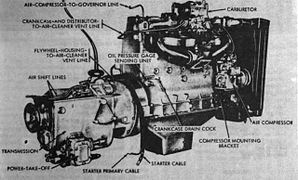
Continental R6602
(right side)
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6CTA8.3[5] | 504 cu in (8.3 L) | D | TC I6 | 240 hp (179 kW) @2100rpm | 745 lbf⋅ft (1,010 N⋅m) @1500rpm | M939 5-ton 6×6 |
| NH250[6] | 855 cu in (14.0 L) | D | I6 | 240 hp (179 kW) @2100rpm | 560 lbf⋅ft (759 N⋅m) @6500rpm | M809 5-ton 6×6), M939 5-ton 6×6 |
| NTC400[7] | 855 cu in (14.0 L) | D | TC I6 | 400 hp (298 kW) @2100rpm | 1,150 lbf⋅ft (1,559 N⋅m) @1500rpm | M915 series 6×4, 6×6, 8×6 |
| V8-300[8] | 785 cu in (12.9 L) | D | V8 | 300 hp (224 kW) @3000rpm |
580 lbf⋅ft (786 N⋅m) @2100rpm |
M123/125 10-ton 6×6 |
-

Cummins 6CTA8.3
(left side) -

Cummins 6CTA8.3
(right side) -
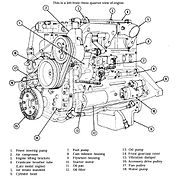
Cummins NH250
(left front) -

Cummins NH250
(right rear) -

Cummins V8-300
(left front) -

Cummins V8-300
(right rear)
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-53 | 159 cu in (2.6 L) | D | SC I3 | 103 hp (77 kW) @2800rpm | 217 lbf⋅ft (294 N⋅m) @1500rpm | M561 1+1⁄2-ton 6×6 “Gamma-goat” |
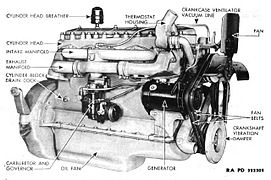
| Series 60 | 775 cu in (12.7 L) | D | TC I6 | 400 hp (298 kW) @2100rpm | 1,400 lbf⋅ft (1,898 N⋅m) @1200rpm | M915 series 6×4, 6×6, 8×6 |
| 8V92TA[9] | 736 cu in (12.1 L) | D | TC V8 | 450 hp (336 kW) | 1,330 lbf⋅ft (1,803 N⋅m) @1200rpm | M911(C-HET) M977(HEMTT), M1070(HET) |
| 12V71 | 852 cu in (14.0 L) | D | SC V12 | 600 hp (447 kW) @2500rpm | 1,470 lbf⋅ft (1,993 N⋅m) @16000rpm | M746 22+1⁄2-ton 8×8 (HET) |
-

-

Detroit Diesel Series 60 (left front)
-
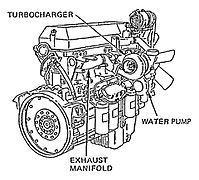
Detroit Diesel Series 60 (right rear)
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-202 | 201 cu in (3.3 L) | G | I6 | 79 hp (59 kW) @3000rpm | VC 1⁄2-ton 4×4 | |
| T-214-245 | 230 cu in (3.8 L) | G | I6 | 92 hp (69 kW) @3200 |
180 lbf⋅ft (244 N⋅m) @1200rpm |
Dodge WC 3⁄4-ton 4×4, M37 3⁄4-ton 4×4 |
| 318[10] | 318 cu in (5.2 L) | G | V8 | 150 hp (112 kW) @4000rpm | 230 lbf⋅ft (312 N⋅m) @2400rpm | M880 1+1⁄4-ton 4×4 (CUCV) |
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTB | 226 cu in (3.7 L) | G | I6 | 90 hp (67 kW) @3000rpm | 180 lbf⋅ft (244 N⋅m) @1200rpm | 1+1⁄2-ton 4×4 |
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 440 | 1,090 cu in (17.9 L) | G | I6 | 240 hp (179 kW) @2000rpm | 810 lbf⋅ft (1,098 N⋅m) @1200rpm | M25 Tank Transporter |
-

Hall-Scott 440 (left side)
-

Hall-Scott 440 (right side)
-

Hercules DFXE (left side)
-

Hercules DFXE (right side)
-

Hercules HXD (left front)
-
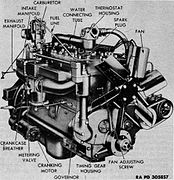
Hercules HXD (right front)
-

-

Hercules JXD (right side)
-

-

Ordnance design LDT-465
(left front) -

Ordnance design LDT-465
(right rear) -

-

Hercules RXC (right side)
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRD-214 | 214 cu in (3.5 L) | G | I6 | 85 hp (63 kW) @3400rpm | 160 lbf⋅ft (217 N⋅m) @1200 | IHC M-1-4 1⁄2-ton 4×4 |
| GRD-233 | 233 cu in (3.8 L) | G | I6 | 93 hp (69 kW) @3400 | 181 lbf⋅ft (245 N⋅m) @800 | IHC M-1-4 1⁄2-ton 4×4, IHC M-5-6 1+1⁄2-ton 6×6 |
| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-H844 | 844 cu in (13.8 L) | G | V8 | 297 hp (221 kW) @2600rpm | 725 lbf⋅ft (983 N⋅m) @1700rpm | M123/25 10-ton 6×6 |
-
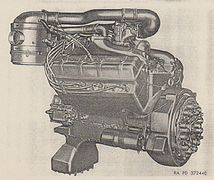
-
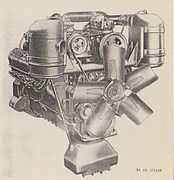
LeRoi T-H844 (right front)
-

-

Mack ENDT673 (right side)
-

| Model | Displacement | Fuel | Type | Power | Torque | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA-331 | 331 cu in (5.4 L) | G | I6 | 146 hp (109 kW) @3400rpm | 330 lbf⋅ft (447 N⋅m) | M35 21⁄2-ton 6×6 |
- ^ a b Army Ordinance design built by AM General and Continental
- ^ a b c d Army Ordnance design built by Continental and Hercules/White.
References[edit]
- ^ TM 9-2320-272-24-4 Unit, Direct Support, and General Support Maintenance Manual for Truck 5 ton, 6×6, M939, M939A1, M939A2 Series (Diesel) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1992. p. 5-157 to 5-279. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2815-237-34 Direct Support and General Support Maintenance Manual…Engine, Diesel: 8 Cylinder…DDA Model 6.2 Liter…DDA 6.5 Liter (and others) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 2004. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ a b TM 9-2815-218-34-1 Direct Support and General Support Maintenance Truck, 1/4-ton, 4×4, M181A2 Series (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1983. p. 3-1 to 3-181. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ a b TM 9-2815-210-34-2-1 Maintenance, Direct Support and General Support Level Engine Assembly, Diesel (Multifuel)…Models: LD-465-1 (and others) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1981. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2320-272-24-4 Unit, Direct Support, and General Support Maintenance Manual for Truck 5 ton, 6×6, M939, M939A1, M939A2 Series (Diesel) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1992. p. 5-157 to 5-279. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2320-260-34-1 Direct Support and General Support Maintenance for 5-ton, 6×6, M809 Series Trucks (Diesel) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1994. p. 3-1 to 3-259. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2815-225-34&P Direct Support and General Support Maintenance Manual…Engine, Diesel: 6 Cylinder In-line Turbocharged, Cummins Model NTC-400 (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 2005. p. 0002 00-1. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2815-213-34 Direct Support and General Support Maintenance Manual…for Engine, Diesel, With Accessories Cummins Model V8-300 (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1972. p. 1-1. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2815-224-34&P Direct Support and General Support Maintenance Manual…Engine, Diesel: 6 Cylinder In-line Turbocharged,Detroit Diesel Corp. Model 8V92TA (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1988. p. 1-7. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
- ^ TM 9-2815-266-34 Direct and General Support Maintenance Manual Truck, Cargo; 1 1/4 Ton M880 (and others) (PDF). US Dept. of the Army. 1986. p. 1-3, 1-4, Chap. 11. Retrieved 23 Jun 2019.
Works cited[edit]





Recent Comments