Timeline of the Golden Horde
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
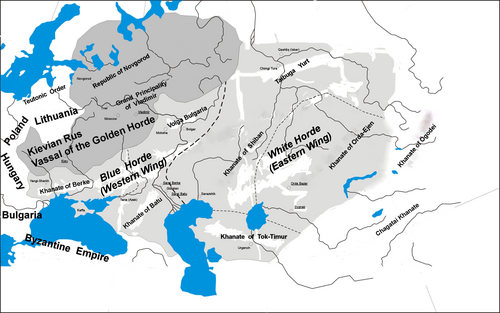
The Golden Horde as it was governed under the dual khanship of the Western and Eastern Wings. When the Golden Horde was founded, it was jointly ruled by two separate wings. The right wing in the west was ruled by Batu Khan and his descendants. The left wing in the east, also known as the “Blue Horde” by the Russians or the “White Horde” by the Timurids, was ruled by four Jochid khans under Orda Khan.

This is a timeline of events involving the Golden Horde (1242–1502), from 1459 also known as the Great Horde.
13th century[edit]
For pre-1242 events involving Mongols in Europe, see Timeline of the Mongol Empire § 13th century
1240s[edit]
1250s[edit]
1260s[edit]
1270s[edit]
1280s[edit]
1290s[edit]
14th century[edit]
1300s[edit]
1310s[edit]
1320s[edit]
1330s[edit]
1340s[edit]
1350s[edit]
1360s[edit]
1370s[edit]
1380s[edit]
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1380 | Golden Horde starts passing decrees in Turkish language | |
| 8 September | Battle of Kulikovo: A largely Muscovite army led by Dmitri Donskoi defeated Mongol warlord Mamai in a pyrrhic victory at Kulikovo field. Mamai’s Tverian allies never showed up, his Lithuanian and Riazani allies arrived too late to take part, but did harass the victorious Muscovite troops as they returned to Moscow. | |
| 1381 | Battle of the Kalka River (1381): Tokhtamysh defeated Mamai, becoming the undisputed khan of the Golden Horde, and ending the war of succession that had been raging ever since 1359. | |
| 1382 | 26 August | Siege of Moscow (1382): khan Tokhtamysh of the Golden Horde and his allied Rus’ princes of Tver, Riazan, and Nizhniy Novgorod besieged and sacked Moscow. The princes of Nizhniy Novgorod tricked the Muscovite citizens into surrendering the city, after which Moscow was immediately sacked. Thereafter, Tokhtamysh’ troops sacked surrounding towns including Serpukhov, Pereyaslavl, and Kolomna, and on their way home southwards also the principality of Riazan. |
| 1383 | Tokhtamysh defeats the Lithuanians at Poltava | |
| 1387 | Golden Horde loses control of the Black Sea coast |
1390s[edit]
15th century[edit]
1400s[edit]
1410s[edit]
1420s[edit]
1430s[edit]
1440s[edit]
1450s[edit]
1460s[edit]
1470s[edit]
1480s[edit]
| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1480 | 8 October – 28 November | Great Stand on the Ugra River: armies of Muscovy and the Great Horde confronted each other without fighting and then simultaneously retreated. Although long hailed as the “end of the Tatar yoke” in traditional Russian historiography, the event changed little in Muscovite–Horde relations. |
16th century[edit]
Gallery[edit]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Bibliography[edit]
- Andrade, Tonio (2016), The Gunpowder Age: China, Military Innovation, and the Rise of the West in World History, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-13597-7.
- Asimov, M.S. (1998), History of civilizations of Central Asia Volume IV The age of achievement: A.D. 750 to the end of the fifteenth century Part One The historical, social and economic setting, UNESCO Publishing
- Atwood, Christopher P. (2004), Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, Facts On File
- Barfield, Thomas (1989), The Perilous Frontier: Nomadic Empires and China, Basil Blackwell
- Barrett, Timothy Hugh (2008), The Woman Who Discovered Printing, Great Britain: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-12728-7 (alk. paper)
- Beckwith, Christopher I. (2009), Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-13589-2
- Beckwith, Christopher I (1987), The Tibetan Empire in Central Asia: A History of the Struggle for Great Power among Tibetans, Turks, Arabs, and Chinese during the Early Middle Ages, Princeton University Press
- Biran, Michal (2005), The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the Islamic World, Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization, Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521842263
- Bregel, Yuri (2003), An Historical Atlas of Central Asia, Brill
- Christian, David (2018), A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia 2, Wiley Blackwell
- Cosmo, Nicola di (2009), The Cambridge History of Inner Asia: The Chinggisid Age, Cambridge University Press
- Crummey, Robert O. (2014). The Formation of Muscovy 1300 – 1613. Routledge. pp. 52–62. (originally published in 1987).
- Drompp, Michael Robert (2005), Tang China And The Collapse Of The Uighur Empire: A Documentary History, Brill
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (1999), The Cambridge Illustrated History of China, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-66991-X (paperback).
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley; Walthall, Anne; Palais, James B. (2006), East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History, Boston: Houghton Mifflin, ISBN 0-618-13384-4
- Golden, Peter B. (1992), An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples: Ethnogenesis and State-Formation in Medieval and Early Modern Eurasia and the Middle East, OTTO HARRASSOWITZ · WIESBADEN
- Graff, David A. (2002), Medieval Chinese Warfare, 300-900, Warfare and History, London: Routledge, ISBN 0415239559
- Graff, David Andrew (2016), The Eurasian Way of War Military Practice in Seventh-Century China and Byzantium, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-46034-7.
- Grousset, Rene (1970), Empire of the Steppes, Rutgers University Press
- Halperin, Charles J. (1987). Russia and the Golden Horde: The Mongol Impact on Medieval Russian History. p. 222. ISBN 9781850430575. (e-book).
- Haywood, John (1998), Historical Atlas of the Medieval World, AD 600-1492, Barnes & Noble
- Jackson, Peter (2005), The Mongols and the West, Pearson Education Limited
- Latourette, Kenneth Scott (1964), The Chinese, their history and culture, Volumes 1-2, Macmillan
- Lorge, Peter A. (2008), The Asian Military Revolution: from Gunpowder to the Bomb, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-60954-8
- Luttwak, Edward N. (2009), The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire, The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press
- Millward, James (2009), Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang, Columbia University Press
- Mote, F. W. (2003), Imperial China: 900–1800, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0674012127
- Needham, Joseph (1986), Science & Civilisation in China, vol. V:7: The Gunpowder Epic, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-30358-3
- Nicol, Donald M. (1993), The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261-1453, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9780521439916
- Rong, Xinjiang (2013), Eighteen Lectures on Dunhuang, Brill
- Schafer, Edward H. (1985), The Golden Peaches of Samarkand: A study of T’ang Exotics, University of California Press
- Shaban, M. A. (1979), The ʿAbbāsid Revolution, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-29534-3
- Shaikhutdinov, Marat (23 November 2021). “3.4 Invasion of Tokhtamysh”. Between East and West: The Formation of the Moscow State. Academic Studies Press. pp. 104–107.
- Sinor, Denis (1990), The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia, Volume 1, Cambridge University Press
- Sima, Guang (2015), Bóyángbǎn Zīzhìtōngjiàn 54 huánghòu shīzōng 柏楊版資治通鑑54皇后失蹤, Yuǎnliú chūbǎnshìyè gǔfèn yǒuxiàn gōngsī, ISBN 978-957-32-0876-1
- Skaff, Jonathan Karam (2012), Sui-Tang China and Its Turko-Mongol Neighbors: Culture, Power, and Connections, 580-800 (Oxford Studies in Early Empires), Oxford University Press
- Standen, Naomi (2007), Unbounded Loyalty Frontier Crossings in Liao China, University of Hawai’i Press
- Steinhardt, Nancy Shatzman (1997), Liao Architecture, University of Hawaii Press
- Twitchett, Denis C. (1979), The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 3, Sui and T’ang China, 589–906, Cambridge University Press
- Twitchett, Denis (1994), “The Liao”, The Cambridge History of China, Volume 6, Alien Regime and Border States, 907-1368, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 43–153, ISBN 0521243319
- Twitchett, Denis (2009), The Cambridge History of China Volume 5 The Sung dynasty and its Predecessors, 907-1279, Cambridge University Press
- Vernadsky, George (1953), The Mongols and Russia, Yale University Press
- Wang, Zhenping (2013), Tang China in Multi-Polar Asia: A History of Diplomacy and War, University of Hawaii Press
- Wilkinson, Endymion (2015). Chinese History: A New Manual, 4th edition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Asia Center distributed by Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674088467.
- Xiong, Victor Cunrui (2000), Sui-Tang Chang’an: A Study in the Urban History of Late Medieval China (Michigan Monographs in Chinese Studies), U OF M CENTER FOR CHINESE STUDIES, ISBN 0892641371
- Xiong, Victor Cunrui (2009), Historical Dictionary of Medieval China, United States of America: Scarecrow Press, Inc., ISBN 978-0810860537
- Xu, Elina-Qian (2005), HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE PRE-DYNASTIC KHITAN, Institute for Asian and African Studies 7
- Xue, Zongzheng (1992), Turkic peoples, 中国社会科学出版社
- Yuan, Shu (2001), Bóyángbǎn Tōngjiàn jìshìběnmò 28 dìèrcìhuànguánshídài 柏楊版通鑑記事本末28第二次宦官時代, Yuǎnliú chūbǎnshìyè gǔfèn yǒuxiàn gōngsī, ISBN 957-32-4273-7
- Yule, Henry (1915), Cathay and the Way Thither: Being a Collection of Medieval Notices of China, Vol I: Preliminary Essay on the Intercourse Between China and the Western Nations Previous to the Discovery of the Cape Route, Hakluyt Society
Recent Comments