Topology optimization – Wikipedia
Mathematical method for optimizing material layout under given conditions
Topology optimization (TO) is a mathematical method that optimizes material layout within a given design space, for a given set of loads, boundary conditions and constraints with the goal of maximizing the performance of the system. Topology optimization is different from shape optimization and sizing optimization in the sense that the design can attain any shape within the design space, instead of dealing with predefined configurations.
The conventional topology optimization formulation uses a finite element method (FEM) to evaluate the design performance. The design is optimized using either gradient-based mathematical programming techniques such as the optimality criteria algorithm and the method of moving asymptotes or non gradient-based algorithms such as genetic algorithms.
Topology optimization has a wide range of applications in aerospace, mechanical, bio-chemical and civil engineering. Currently, engineers mostly use topology optimization at the concept level of a design process. Due to the free forms that naturally occur, the result is often difficult to manufacture. For that reason the result emerging from topology optimization is often fine-tuned for manufacturability. Adding constraints to the formulation in order to increase the manufacturability is an active field of research. In some cases results from topology optimization can be directly manufactured using additive manufacturing; topology optimization is thus a key part of design for additive manufacturing.
Problem statement[edit]
A topology optimization problem can be written in the general form of an optimization problem as:
The problem statement includes the following:
- An objective function . This function represents the quantity that is being minimized for best performance. The most common objective function is compliance, where minimizing compliance leads to maximizing the stiffness of a structure.
- The material distribution as a problem variable. This is described by the density of the material at each location . Material is either present, indicated by a 1, or absent, indicated by a 0. is a state field that satisfies a linear or nonlinear state equation depending on .
- The design space . This indicates the allowable volume within which the design can exist. Assembly and packaging requirements, human and tool accessibility are some of the factors that need to be considered in identifying this space . With the definition of the design space, regions or components in the model that cannot be modified during the course of the optimization are considered as non-design regions.
- constraints a characteristic that the solution must satisfy. Examples are the maximum amount of material to be distributed (volume constraint) or maximum stress values.
Evaluating
often includes solving a differential equation. This is most commonly done using the finite element method since these equations do not have a known analytical solution.
Implementation methodologies[edit]
There are various implementation methodologies that have been used to solve topology optimization problems.
Discrete[edit]
Solving topology optimization problems in a discrete sense is done by discretizing the design domain into finite elements. The material densities inside these elements are then treated as the problem variables. In this case material density of one indicates the presence of material, while zero indicates an absence of material. Owing to the attainable topological complexity of the design being dependent on the number of elements, a large number is preferred. Large numbers of finite elements increases the attainable topological complexity, but come at a cost. Firstly, solving the FEM system becomes more expensive. Secondly, algorithms that can handle a large number (several thousands of elements is not uncommon) of discrete variables with multiple constraints are unavailable. Moreover, they are impractically sensitive to parameter variations.[1] In literature problems with up to 30000 variables have been reported.[2]
Solving the problem with continuous variables[edit]
The earlier stated complexities with solving topology optimization problems using binary variables has caused the community to search for other options. One is the modelling of the densities with continuous variables. The material densities can now also attain values between zero and one. Gradient based algorithms that handle large amounts of continuous variables and multiple constraints are available. But the material properties have to be modelled in a continuous setting. This is done through interpolation. One of the most implemented interpolation methodologies is the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalisation method (SIMP).[3][4] This interpolation is essentially a power law
. It interpolates the Young’s modulus of the material to the scalar selection field. The value of the penalisation parameter
is generally taken between
. This has been shown to confirm the micro-structure of the materials.[5] In the SIMP method a lower bound on the Young’s modulus is added,
, to make sure the derivatives of the objective function are non-zero when the density becomes zero. The higher the penalisation factor, the more SIMP penalises the algorithm in the use of non-binary densities. Unfortunately, the penalisation parameter also introduces non-convexities.[6]
Shape derivatives[edit]
Topology optimization can be achieved by using shape derivatives.
Topological derivatives[edit]
Level set[edit]
Phase field[edit]
Evolutionary structural optimization[edit]
Commercial software[edit]
There are several commercial topology optimization software on the market. Most of them use topology optimization as a hint how the optimal design should look like, and manual geometry re-construction is required. There are a few solutions which produce optimal designs ready for Additive Manufacturing.
Examples[edit]
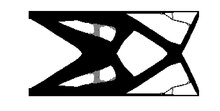


Structural compliance[edit]
A stiff structure is one that has the least possible displacement when given certain set of boundary conditions. A global measure of the displacements is the strain energy (also called compliance) of the structure under the prescribed boundary conditions. The lower the strain energy the higher the stiffness of the structure. So, the objective function of the problem is to minimize the strain energy.
On a broad level, one can visualize that the more the material, the less the deflection as there will be more material to resist the loads. So, the optimization requires an opposing constraint, the volume constraint. This is in reality a cost factor, as we would not want to spend a lot of money on the material. To obtain the total material utilized, an integration of the selection field over the volume can be done.
Finally the elasticity governing differential equations are plugged in so as to get the final problem statement.
subject to:
But, a straightforward implementation in the finite element framework of such a problem is still infeasible owing to issues such as:
- Mesh dependency—Mesh Dependency means that the design obtained on one mesh is not the one that will be obtained on another mesh. The features of the design become more intricate as the mesh gets refined.[7]
- Numerical instabilities—The selection of region in the form of a chess board.[8]
Some techniques such as filtering based on image processing[9] are currently being used to alleviate some of these issues. Although it seemed like this was purely a heuristic approach for a long time, theoretical connections to nonlocal elasticity have been made to support the physical sense of these methods.[10]
Multiphysics problems[edit]
Fluid-structure-interaction[edit]
Fluid-structure-interaction is a strongly coupled phenomenon and concerns the interaction between a stationary or moving fluid and an elastic structure. Many engineering applications and natural phenomena are subject to fluid-structure-interaction and to take such effects into consideration is therefore critical in the design of many engineering applications. Topology optimisation for fluid structure interaction problems has been studied in e.g. references[11][12][13] and.[14] Design solutions solved for different Reynolds numbers are shown below. The design solutions depend on the fluid flow with indicate that the coupling between the fluid and the structure is resolved in the design problems.
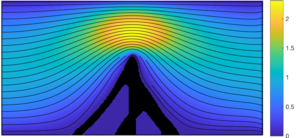
Design solution and velocity field for Re=1

Design solution and velocity field for Re=5

Design solution and pressure field for Re=10

Design solution and pressure field for Re=40
Design solutions for different Reynolds number for a wall inserted in a channel with a moving fluid.


Thermoelectric energy conversion[edit]



Thermoelectricity is a multi-physic problem which concerns the interaction and coupling between electric and thermal energy in semi conducting materials. Thermoelectric energy conversion can be described by two separately identified effects: The Seebeck effect and the Peltier effect. The Seebeck effect concerns the conversion of thermal energy into electric energy and the Peltier effect concerns the conversion of electric energy into thermal energy.[15] By spatially distributing two thermoelectric materials in a two dimensional design space with a topology optimisation methodology,[16] it is possible to exceed performance of the constitutive thermoelectric materials for thermoelectric coolers and thermoelectric generators.[17]
3F3D Form Follows Force 3D Printing[edit]
The current proliferation of 3D printer technology has allowed designers and engineers to use topology optimization techniques when designing new products. Topology optimization combined with 3D printing can result in less weight, improved structural performance and shortened design-to-manufacturing cycle. As the designs, while efficient, might not be realisable with more traditional manufacturing techniques.[citation needed]
Design-dependent loads[edit]
The direction, magnitude, and location of a design-dependent load alter with topology optimization iterations. Therefore, dealing with such loads in a TO setting is a challenging task. One can find novel methods to deal with such loads (e.g. pressure load, self-weight, etc) in Refs.[18][19][20]
References[edit]
- ^ Sigmund, Ole; Maute, Kurt (2013). “Topology optimization approaches”. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 48 (6): 1031–1055. doi:10.1007/s00158-013-0978-6. S2CID 124426387.
- ^ Beckers, M. (1999). “Topology optimization using a dual method with discrete variables” (PDF). Structural Optimization. 17: 14–24. doi:10.1007/BF01197709. S2CID 122845784.
- ^ Bendsøe, M. P. (1989). “Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem”. Structural Optimization. 1 (4): 193–202. doi:10.1007/BF01650949. S2CID 18253872.
- ^ [1], a monograph of the subject.
- ^ Bendsøe, M. P.; Sigmund, O. (1999). “Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization” (PDF). Archive of Applied Mechanics. 69 (9–10): 635–654. Bibcode:1999AAM….69..635B. doi:10.1007/s004190050248. S2CID 11368603.
- ^ van Dijk, NP. Langelaar, M. van Keulen, F. Critical study of design parameterization in topology optimization; The influence of design parameterization on local minima.. 2nd International Conference on Engineering Optimization, 2010
- ^ Allaire, Grégoire; Henrot, Antoine (May 2001). “On some recent advances in shape optimization”. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Series IIB – Mechanics. Elsevier. 329 (5): 383–396. doi:10.1016/S1620-7742(01)01349-6. ISSN 1620-7742. Retrieved 2021-09-12.
- ^ Shukla, Avinash; Misra, Anadi; Kumar, Sunil (September 2013). “Checkerboard Problem in Finite Element Based Topology Optimization”. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology. CiteSeer. 6 (4): 1769–1774. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.670.6771. ISSN 2231-1963. Retrieved 2022-02-14.
- ^ Bourdin, Blaise (2001-03-30). “Filters in topology optimization”. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. Wiley. 50 (9): 2143–2158. doi:10.1002/nme.116. ISSN 1097-0207. Retrieved 2020-08-02.
- ^ Sigmund, Ole; Maute, Kurt (October 2012). “Sensitivity filtering from a continuum mechanics perspective”. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. Springer. 46 (4): 471–475. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0814-4. ISSN 1615-1488. Retrieved 2021-06-17.
- ^ Yoon, Gil Ho (2010). “Topology optimization for stationary fluid-structure interaction problems using a new monolithic formulation”. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. 82 (5): 591–616. Bibcode:2010IJNME..82..591Y. doi:10.1002/nme.2777.
- ^ Picelli, R.; Vicente, W.M.; Pavanello, R. (2017). “Evolutionary topology optimization for structural compliance minimization considering design-dependent FSI loads”. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design. 135: 44–55. doi:10.1016/j.finel.2017.07.005.
- ^ Jenkins, Nicholas; Maute, Kurt (2016). “An immersed boundary approach for shape and topology optimization of stationary fluid-structure interaction problems”. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 54 (5): 1191–1208. doi:10.1007/s00158-016-1467-5. S2CID 124632210.
- ^ a b Lundgaard, Christian; Alexandersen, Joe; Zhou, Mingdong; Andreasen, Casper Schousboe; Sigmund, Ole (2018). “Revisiting density-based topology optimization for fluid-structure-interaction problems” (PDF). Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 58 (3): 969–995. doi:10.1007/s00158-018-1940-4. S2CID 125798826.
- ^ Rowe, David Michael. Thermoelectrics handbook: macro to nano. CRC press, 2005.
- ^ Lundgaard, Christian; Sigmund, Ole (2018). “A density-based topology optimization methodology for thermoelectric energy conversion problems” (PDF). Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 57 (4): 1427–1442. doi:10.1007/s00158-018-1919-1. S2CID 126031362.
- ^ Lundgaard, Christian; Sigmund, Ole; Bjørk, Rasmus (2018). “Topology Optimization of Segmented Thermoelectric Generators”. Journal of Electronic Materials. 47 (12): 6959–6971. Bibcode:2018JEMat..47.6959L. doi:10.1007/s11664-018-6606-x. S2CID 105113187.
- ^ Kumar, P; Frouws, J S; Langelaar, M (2020). “Topology optimization of fluidic pressure-loaded structures and compliant mechanisms using the Darcy method”. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 61 (4): 1637–1655. arXiv:1909.03292. doi:10.1007/s00158-019-02442-0.
- ^ Kumar, P; Langelaar, M (2021). “On topology optimization of design‐dependent pressure‐loaded three‐dimensional structures and compliant mechanisms”. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. 122 (9): 2205–2220. arXiv:2009.05839. doi:10.1002/nme.6618.
- ^ Kumar, P (2022). “Topology optimization of stiff structures under self-weight for given volume using a smooth Heaviside function”. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. 65 (4): 1–17. arXiv:2111.13875. doi:10.1007/s00158-022-03232-x.
Further reading[edit]
- Recent Developments in the Commercial Implementation of Topology Optimization; Uwe Schramm, Ming Zhou; IUTAM Symposium on Topological Design Optimization of Structures, Machines and Materials: Status and Perspectives, 239–248; 2006 Springer.
- Industrial Implementation and Applications of Topology Optimization and Future Needs; Claus B.W. Pedersen; Peter Allinger; IUTAM Symposium on Topological Design Optimization of Structures, Machines and Materials, 229-238; 2006 Springer.
- Topology optimization of 2D continua for minimum compliance using parallel computing Arash Mahdavi; Balaji Raghavan; Mary Frecker; Int Journal of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, Volume 32, 121-132, 2006 Springer
- Modern Structural Optimization Concepts Applied to Topology Optimization Juan Pablo Leiva; Brian C. Watson and Iku Kosaka ; 40th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Material Conference. St. Louis, MO, pp. 1589–1596, 1999








 often includes solving a differential equation. This is most commonly done using the finite element method since these equations do not have a known analytical solution.
often includes solving a differential equation. This is most commonly done using the finite element method since these equations do not have a known analytical solution.
 . It interpolates the Young’s modulus of the material to the scalar selection field. The value of the penalisation parameter
. It interpolates the Young’s modulus of the material to the scalar selection field. The value of the penalisation parameter  is generally taken between
is generally taken between ![{displaystyle [1,,3]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2db1d93f4742c458a144802d4f79c6273fd70cae) . This has been shown to confirm the micro-structure of the materials.[5] In the SIMP method a lower bound on the Young’s modulus is added,
. This has been shown to confirm the micro-structure of the materials.[5] In the SIMP method a lower bound on the Young’s modulus is added,  , to make sure the derivatives of the objective function are non-zero when the density becomes zero. The higher the penalisation factor, the more SIMP penalises the algorithm in the use of non-binary densities. Unfortunately, the penalisation parameter also introduces non-convexities.[6]
, to make sure the derivatives of the objective function are non-zero when the density becomes zero. The higher the penalisation factor, the more SIMP penalises the algorithm in the use of non-binary densities. Unfortunately, the penalisation parameter also introduces non-convexities.[6]
![{displaystyle rho ,in ,[0,,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0e8e9020862238406bc8f1a86e05872c57d96367)



Recent Comments